Last Updated On : 13-Jan-2026
Total 166 Questions
Which SQL query is in the correct order to query the database in the FortiAnslyzer?
A. SELECT devid FROM Slog GROOP BY devid WHERE * user' =* USERl'
B. SELECT devid WHERE 'u3er'='USERl' FROM $ log GROUP BY devid
C. SELECT devid FROM Slog- WHERE *user' =' USERl' GROUP BY devid
D. FROM Slog WHERE 'user* =' USERl' SELECT devid GROUP BY devid
Summary
FortiAnalyzer allows the use of custom SQL queries within datasets to create highly specific reports. These queries must follow the standard syntax rules of the SQL language. The correct sequence of clauses in a basic SQL SELECT statement is: SELECT, FROM, WHERE, and then GROUP BY. Any deviation from this standard order will result in a syntax error.
Correct Option
C. SELECT devid FROM Slog WHERE 'user'='USER1' GROUP BY devid
This is correct. This query follows the proper SQL clause order:
SELECT devid: Specifies the column to retrieve.
FROM Slog: Specifies the database table to query.
WHERE 'user'='USER1': Applies a filter to only include rows where the 'user' column equals 'USER1'.
GROUP BY devid: Groups the results by the 'devid' column.
Incorrect Option
**A. SELECT devid FROM Slog GROOP BY devid WHERE 'user' = 'USER1'**
This is incorrect for two reasons. First, the keywordGROUP BYis misspelled asGROOP BY. Second, even if spelled correctly, theWHEREclause must come *before* theGROUP BY` clause in a SQL statement.
B. SELECT devid WHERE 'user'='USER1' FROM Slog GROUP BY devid
This is incorrect because the clause order is wrong. The FROM clause, which defines the table, must immediately follow the SELECT clause or come after it, not be placed after the WHERE clause.
D. FROM Slog WHERE 'user'='USER1' SELECT devid GROUP BY devid
This is incorrect because it does not start with the SELECT clause. Every SQL query that retrieves data must begin with SELECT to define which columns are being returned.
Reference
Fortinet Documentation Library: SQL syntax for datasets (This section outlines the requirements and structure for writing valid SQL queries for use in FortiAnalyzer datasets).
Refer to the exhibit.
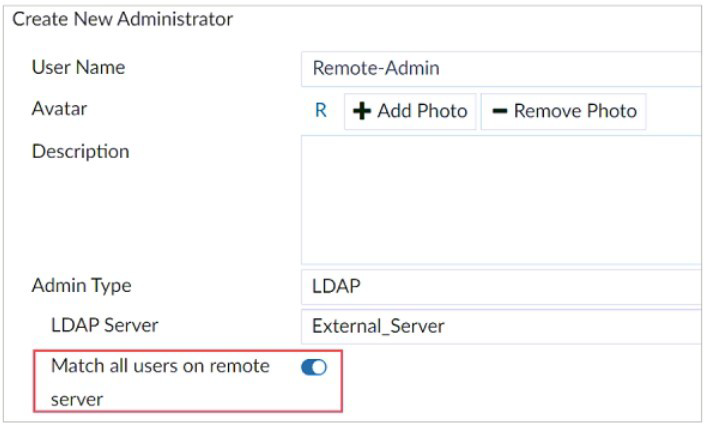
The exhibit shows the creation of a new administrator on FortiAnalyzer.
What are two effects of enabling the choice Match all users on remote server when
configuring a new administrator? (Choose two.)
A. It allows user accounts in the LDAP server to use two-factor authentication.
B. It creates a wildcard administrator using an LDAP server.
C. User Remote-Admin from the LDAP server will be able to log in to FortiAnalyzer at any time.
D. Administrators can log in to FortiAnalyzer using their credentials on the remote LDAP server.
Summary
The "Match all users on remote server" option is a powerful feature when configuring LDAP administrator authentication on FortiAnalyzer. Instead of mapping a single LDAP user to a single FortiAnalyzer admin account, it creates a rule that grants administrative access based on group membership or a general match within the LDAP directory, effectively allowing multiple users from the remote server to log in.
Correct Option
B. It creates a wildcard administrator using an LDAP server.
This is correct. Enabling this option essentially creates a wildcard or template. It tells the FortiAnalyzer that any user who successfully authenticates against the specified LDAP server and is a member of the configured LDAP group (if specified) should be granted the administrator permissions (profile and ADOM access) defined in this configuration entry. It does not require a one-to-one mapping for each user.
D. Administrators can log in to FortiAnalyzer using their credentials on the remote LDAP server.
This is correct. This is the primary function. Once this is configured, users who exist in the LDAP directory can use their standard LDAP username and password to log into the FortiAnalyzer. Their access level and permissions within FortiAnalyzer are determined by the administrator profile and ADOM assignments configured in this "wildcard" administrator entry.
Incorrect Option
A. It allows user accounts in the LDAP server to use two-factor authentication.
This is incorrect. The ability to use two-factor authentication (2FA) is determined by the configuration on the LDAP server itself or a linked service (like RADIUS with an authenticator). The "Match all users" option on FortiAnalyzer only dictates which LDAP users are allowed to authenticate; it does not enable or disable 2FA capabilities. The FortiAnalyzer simply passes the credentials to the LDAP server for validation.
C. User Remote-Admin from the LDAP server will be able to log in to FortiAnalyzer at any time.
This is misleading and therefore incorrect. The username configured in the "User Name" field ("Remote-Admin" in this case) becomes the name of the administrator configuration entry on FortiAnalyzer, not the specific LDAP username. The actual users who can log in are those in the LDAP directory, not a single user named "Remote-Admin". Furthermore, their ability to log in is always subject to the LDAP server being available and their account being active.
Reference
Fortinet Documentation Library: Administrators (This section explains the configuration of different admin types, including LDAP and the "Match all users" option).
What does the disk status Degraded mean for RAID management?
A. The hard drive is no longer being used by the RAID controller.
B. One or more drives are missing from the FortiAnalyzer unit.
C. The device is writing data to the disk to restore the volume to an optimal state.
D. FortiAnalyzer determined that the parity data in the disk is not valid.
Summary
In RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) management, the term "Degraded" has a specific and critical meaning. It indicates that the fault tolerance of the RAID array has been compromised because one of the physical disks in the array has failed. The system remains operational by using the remaining good disk(s), but it is now vulnerable to a second disk failure.
Correct Option
B. One or more drives are missing from the FortiAnalyzer unit.
This is correct. A "Degraded" status means that the RAID array has detected a physical disk failure or that a disk is missing. The array is still functional because it can read from and write to the remaining healthy disk(s), but it is operating without its full redundancy. This state requires immediate attention to replace the failed drive.
Incorrect Option
A. The hard drive is no longer being used by the RAID controller.
This is too vague. While a failed drive is no longer actively used for read/write operations in a degraded array, this description doesn't capture the critical state of lost redundancy. "Degraded" specifically describes the state of the entire array, not just the status of a single component.
C. The device is writing data to the disk to restore the volume to an optimal state.
This is incorrect. This process describes a "Rebuilding" or "Resyncing" state. After a failed drive is replaced with a new one, the RAID controller enters a "Rebuilding" state, where it reconstructs the data onto the new disk. "Degraded" is the state before and during the rebuild, when the array is still vulnerable.
D. FortiAnalyzer determined that the parity data in the disk is not valid.
This is incorrect. This description might relate to a data consistency error or checksum failure on a specific disk. The "Degraded" status is a hardware-level state reported by the RAID controller indicating a physical disk failure or removal, not a logical data corruption issue.
Reference
Fortinet Documentation Library: Monitoring hardware (This section covers monitoring disk and RAID status, including interpreting states like Degraded).
Which two purposes does the auto cache setting on reports serve? (Choose two.)
A. It automatically updates the hcache when new logs arrive.
B. It provides diagnostics on report generation time.
C. It reduces the log insert lag rate.
D. It reduces report generation time.
Summary
The Auto Cache feature for reports on FortiAnalyzer is a performance optimization tool. It works by periodically pre-generating and storing (caching) the data for a report according to a set schedule. This shifts the resource-intensive process of querying the database from the moment a user requests the report to a scheduled, off-peak time.
Correct Option
A. It automatically updates the cache when new logs arrive.
This is correct. When Auto Cache is enabled, you configure a schedule (e.g., every hour, daily). The system automatically runs the report's dataset queries according to this schedule, updating the cached data. This ensures the cache is refreshed with new log data without manual intervention, keeping the pre-generated data relatively current.
D. It reduces report generation time.
This is correct. This is the primary purpose of caching. When a user views a report with a valid cache, FortiAnalyzer simply displays the pre-generated results instead of executing a new, resource-intensive query against the live SQL database. This makes the report load almost instantly for the user.
Incorrect Option
B. It provides diagnostics on report generation time.
This is incorrect. While the system may log the time it takes to generate a cache, that is a side effect, not the purpose of the feature. The Auto Cache setting itself is a performance feature, not a diagnostic tool. Diagnostic information is found in system logs and performance monitors.
C. It reduces the log insert lag rate.
This is incorrect. Report generation and log insertion are separate processes. Auto Cache affects report queries run against the already indexed SQL database. Log insert lag is the delay in parsing and inserting new, incoming logs into that database. Caching reports does not directly impact the performance of the sqlplugind daemon responsible for log indexing.
Reference
Fortinet Documentation Library: Report caching (This section explains the purpose and configuration of automatic report caching).
Refer to the exhibit.
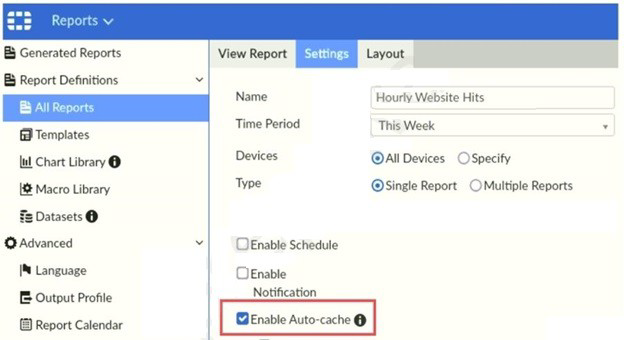
Which two statements are true regarding enabling auto-cache on FortiAnalyzer? (Choose
two.)
A. Report size will be optimized to conserve disk space on FortiAnalyzer.
B. Reports will be cached in the memory.
C. This feature is automatically enabled for scheduled reports.
D. Enabling auto-cache reduces report generation time for reports that require a long time to assemble datasets.
Summary
The Auto-cache feature on FortiAnalyzer is a performance optimization for reports. It works by pre-generating and storing the report data at scheduled intervals. This means the computationally intensive work of querying the database and assembling the datasets is done ahead of time, rather than when a user clicks to view the report.
Correct Option
B. Reports will be cached in the memory.
This is correct. While the report definition and schedule are stored on disk, the actual cached report data is typically held in the system's memory (RAM) for fast access. This allows for near-instantaneous loading when a user requests to view the report, as the data does not need to be queried from the slower disk-based SQL database.
D. Enabling auto-cache reduces report generation time for reports that require a long time to assemble datasets.
This is correct. This is the primary purpose of auto-cache. For reports that query large volumes of log data, generating the results can take a long time. By pre-generating the cache on a schedule, the final report is ready immediately for the user. The "generation time" experienced by the user is effectively reduced to zero, as they are viewing a pre-computed snapshot.
Incorrect Option
A. Report size will be optimized to conserve disk space on FortiAnalyzer.
This is incorrect. Auto-cache does not optimize or compress the report data to save space. Its goal is performance, not storage efficiency. In fact, caching multiple reports can consume significant system memory, but it is not a disk space conservation feature.
C. This feature is automatically enabled for scheduled reports.
This is incorrect. Auto-cache is not enabled by default. It is an optional setting that an administrator must manually enable for each report definition, as shown in the exhibit with the checkbox "[x] Enable Auto-cache". A report can be scheduled without having auto-cache enabled.
Reference
Fortinet Documentation Library: Report caching (This section explains the auto-cache feature and its manual configuration).
The connection status of a new device on FortiAnalyzer is listed as Unauthorized.
What does that status mean?
A. It is a device whose registration has not yet been accepted in FortiAnalvzer.
B. It is a device that has not yet been assigned an ADOM.
C. It is a device that is waiting for you to configure a pre-shared key.
D. It is a device that FortiAnalvzer does not support.
Summary
The "Unauthorized" status is a specific security state in the device management workflow of FortiAnalyzer. It indicates that a device (like a FortiGate) has attempted to register with the FortiAnalyzer, but an administrator has not yet explicitly approved this connection. This manual approval step prevents unauthorized devices from sending logs to the analyzer.
Correct Option
A. It is a device whose registration has not yet been accepted in FortiAnalyzer.
This is correct. When a new device attempts to connect for the first time, it appears in the device list with an "Unauthorized" status. This is a pending state, requiring an administrator to log into the FortiAnalyzer and explicitly authorize the device. This step ensures that only approved and managed devices can send logs to the system.
Incorrect Option
B. It is a device that has not yet been assigned an ADOM.
This is incorrect. While an unauthorized device is not yet placed in an ADOM, the core issue is the lack of approval, not the ADOM assignment. Once authorized, the device is automatically placed in the root ADOM by default, and the administrator can then move it to a different ADOM if needed. The "Unauthorized" status is specifically about registration acceptance.
C. It is a device that is waiting for you to configure a pre-shared key.
This is incorrect. The pre-shared key is configured on the FortiGate (the client device) in its log settings pointing to the FortiAnalyzer. If the key is incorrect, the connection would typically fail outright or be rejected, not sit in an "Unauthorized" state. The "Unauthorized" status appears after a basic connection is made but before administrative approval is granted.
D. It is a device that FortiAnalyzer does not support.
This is incorrect. An unsupported device would not be able to establish a proper management connection with the FortiAnalyzer in the first place. It would not appear in the device list with any status. The "Unauthorized" status explicitly confirms that the device model and firmware are recognized and supported, but are pending administrative authorization.
Reference
Fortinet Documentation Library: Authorizing devices (This section describes the process of authorizing a device that is in the "Unauthorized" state).
You have recently grouped multiple FortiGate devices into a single ADOM. System
Settings > Storage Info
shows the quota used.
What does the disk quota refer to?
A. The maximum disk utilization for each device in the ADOM
B. The maximum disk utilization for the FortiAnalyzer model
C. The maximum disk utilization for the ADOM type
D. The maximum disk utilization for all devices in the ADOM
| Page 3 out of 24 Pages |
| FCP_FAZ_AD-7.4 Practice Test Home | Previous |
Choosing the right preparation material is critical for passing the Fortinet FCP - FortiAnalyzer 7.4 Administrator exam. Here’s how our FCP_FAZ_AD-7.4 practice test is designed to bridge the gap between knowledge and a passing score.