Last Updated On : 13-Jan-2026
Total 106 Questions
Refer to the exhibit showing a firewall policy configuration.
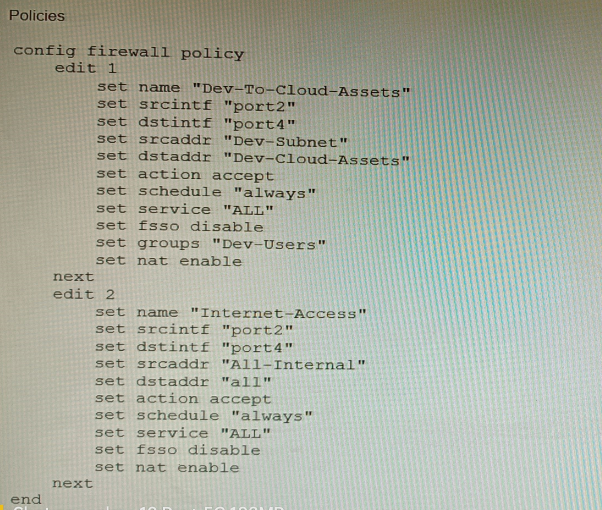
To prevent unauthorized access of their cloud assets, an administrator wants to enforce
authentication on firewall policy ID 1.
What change does the administrator need to make?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Explanation:
The ntlm-guest option is specifically designed to control whether unauthenticated users are allowed. Disabling it ensures all traffic matching the policy requires successful user authentication.
Why other options are incorrect:
A (auth-on-demand always)
enables captive portal but does not enforce mandatory authentication; users can click "Cancel" and pass through.
B (auth-secure-http enable and auth-http-basic disable)
selects HTTPS over HTTP for captive portal but does not enforce authentication for all traffic.
D (fsso enable)
enables Fortinet Single Sign-On, which is a method for passive authentication, but does not enforce active authentication for guest users like ntlm-guest disable does.
Reference:
FortiOS Handbook – Firewall Authentication: The set ntlm-guest disable command forces authentication for all users, blocking unauthenticated (guest) access through the policy.
Refer to the exhibit.

You have deployed a security fabric with three FortiGate devices as shown in the exhibit.
FGT_2 has the following configuration:
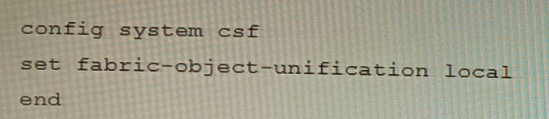
FGT_1 and FGT_3 are configured with the default setting. Which statement is true for the
synchronization of fabric-objects?
A. Objects from the FortiGate FGT_2 will be synchronized to the upstream FortiGate.
B. Objects from the root FortiGate will only be synchronized to FGT__2.
C. Objects from the root FortiGate will not be synchronized to any downstream FortiGate.
D. Objects from the root FortiGate will only be synchronized to FGT_3.
Explanation:
The setting set fabric-object-unification local on FGT_2 configures it to synchronize its locally defined address and service objects upstream to the root FortiGate (FGT_1). Once these objects reach the root, they can be distributed fabric-wide if configured. This is the primary function of the local setting—enabling a downstream device to share its objects upward for potential use by other fabric members. The root and FGT_3 use the default setting (global or default), which means they receive objects from the root but do not push their own upstream.
Why other options are incorrect:
B is incorrect
because the root FortiGate synchronizes its objects to all downstream fabric members by default (both FGT_2 and FGT_3). FGT_2’s local setting does not restrict it from receiving root objects; it only changes FGT_2’s own synchronization direction.
C is false;
the default behavior of the Security Fabric is hierarchical object synchronization, where the root’s objects are synchronized to downstream devices. Nothing in the configuration shown disables this.
D is incorrect;
there is no exclusive synchronization channel. FGT_3 receives objects from the root just as FGT_2 does, because both are downstream members with default (global) unification settings.
Reference:
FortiOS 7.4 Security Fabric Guide – Fabric Object Unification: The local setting allows a downstream FortiGate to publish its local objects to the root FortiGate, while global (default) allows the device to receive objects from the root. The root can propagate obje
On a FortiGate Configured in Transparent mode, which configuration option allows you to
control Multicast traffic passing through the?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Explanation:
In Transparent (Layer 2) mode, the FortiGate forwards multicast frames between interfaces based on the multicast-forward setting. Disabling it (set multicast-forward disable) blocks multicast traffic, while enabling it allows it. This gives explicit administrative control over whether multicast packets pass through the device. The other setting (multicast-skip-policy) is irrelevant in transparent mode as it only applies to multicast routing in NAT mode.
Why other options are incorrect:
A and D (multicast-skip-policy) are invalid because this command only functions in NAT/Route mode. In transparent mode, there are no multicast routes or policies for multicast to skip; the setting has no effect.
B (multicast-forward enable) would permit multicast forwarding, which is the opposite of “controlling” traffic in a security context where blocking or restricting is typically desired. The question implies implementing a control measure, which in firewall terms usually means restricting traffic, making disable the correct choice for establishing control.
Reference:
FortiOS 7.4 Transparent Mode Administration Guide:
The multicast-forward system setting determines whether multicast Layer 2 frames are forwarded between interfaces in transparent mode. This is separate from multicast-skip-policy, which applies only to routed multicast traffic in NAT mode.
A remote worker requests access to an SSH server inside the network. You deployed a
ZTNA Rule to their FortiClient. You need to follow the security requirements to inspect this
traffic.
Which two statements are true regarding the requirements? (Choose two.)
A. FortiGate can perform SSH access proxy host-key validation.
B. You need to configure a FortiClient SSL-VPN tunnel to inspect the SSH traffic.
C. SSH traffic is tunneled between the client and the access proxy over HTTPS
D. Traffic is discarded as ZTNA does not support SSH connection rules
Explanation:
ZTNA architecture tunnels TCP-based applications like SSH between the FortiClient endpoint and the FortiGate access proxy over an HTTPS connection. This allows the FortiGate to inspect the traffic, apply security policies, and perform additional security checks. One such check is SSH host-key validation, where the FortiGate can verify the SSH server’s public key against a preconfigured fingerprint to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks. The ZTNA model ensures encrypted access without requiring a full SSL‑VPN tunnel.
Why other options are incorrect:
B is incorrect because ZTNA does not use SSL‑VPN tunnels; it establishes its own TLS/HTTPS-based tunnel directly between FortiClient and the FortiGate acting as the ZTNA access proxy. SSL‑VPN is a separate remote-access technology with different configuration and packet flow.
D is false; ZTNA explicitly supports SSH through TCP forwarding rules in the ZTNA access proxy configuration. SSH is a common use case documented in Fortinet’s ZTNA deployment guides, and the access proxy can broker and inspect the SSH session.
Reference:
FortiOS 7.4 ZTNA Guide – Access Proxy Configuration: ZTNA access proxy tunnels TCP applications over HTTPS and can validate SSH host keys to ensure server identity. SSH traffic is forwarded through the proxy after authentication and host-key verification, enabling inspection and policy enforcement.
Refer to the exhibit containing the configuration snippets from the FortiGate. Customer
requirements:

• SSLVPN Portal must be accessible on standard HTTPS port (TCP/443)
• Public IP address (129.11.1.100) is assigned to portl
• Datacenter.acmecorp.com resolves to the public IP address assigned to portl
The customer has a Let's Encrypt certificate that is going to expire soon and it reports that
subsequent attempts to renew that certificate are failing.
Reviewing the requirement and the exhibit, which configuration change below will resolve
this issue?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Explanation:
The Let's Encrypt renewal fails because the ACME HTTP-01 challenge requires public access to port 80 on the same IP (129.11.1.100). In the original configuration, port1 hosts SSL‑VPN on port 443 and likely lacks an open HTTP (port 80) responder for ACME validation. Setting set interface "port2" in the ACME configuration redirects renewal traffic to the internal network, where an internal web service or the FortiGate’s built-in ACME responder can properly answer the HTTP challenge without conflicting with the production SSL‑VPN service on port1.
Why other options are incorrect:
A (set https-redirect disable) only stops redirecting HTTP to HTTPS for the SSL‑VPN portal. It does not free port 80 or solve the ACME validation path.
C (appending h-fortigate_public to the firewall policy) merely adds the FortiGate’s public address as a destination for the existing FortiMail policy, which is irrelevant to the ACME renewal process and port accessibility.
D (set admin-port 8080) changes the management GUI port, but ACME challenges target the configured interface’s public IP on standard ports (80/443), not the admin port.
Reference:
FortiOS 7.4 Certificate Management Guide – ACME Integration: For successful renewal, the interface specified in config system acme must have port 80 publicly reachable (for HTTP-01) or port 443 (for TLS-ALPN-01). If the external interface’s ports are occupied, the ACME client should be assigned to a different interface with proper routing/NAT to an internal responder.
Refer to the exhibit.

You are deploying a FortiGate 6000F. The device should be directly connected to a switch.
In the future, a new hardware module providing higher speed will be installed in the switch,
and the connection to the FortiGate must be moved to this higher-speed port.
You must ensure that the initial FortiGate interface connected to the switch does not affect
any other port when the new module is installed and the new port speed is defined.
How should the initial connection be made?
A. Connect the switch on any interface between ports 21 to 24
B. Connect the switch on any interface between ports 25 to 28
C. Connect the switch on any interface between ports 1 to 4
D. Connect the switch on any interface between ports 5 to 8.
Explanation:
On a FortiGate 6000F, ports 1–4 are 1/10/25G SFP28 interfaces, which support multiple speeds through software configuration. This allows the initial connection to be established at a lower speed (e.g., 10G). When the switch’s new high-speed module is installed, the same physical port can be reconfigured to a higher speed (e.g., 25G) by changing the interface’s speed setting in the FortiGate CLI/GUI—without physically moving the cable or affecting neighboring ports. This provides future-proof flexibility and minimizes disruption.
Why other options are incorrect:
A & D (ports 5–8 and 21–24):
While these are also 1/10/25G SFP28 ports and could technically be reconfigured, the question’s scenario calls for a connection that does not affect any other port when the speed is changed. Using ports 1–4 (the first bank) is the logical choice in a staged deployment, as these are often reserved for flexible uplink configurations.
B (ports 25–28):
These are 40/100G QSFP28 interfaces, which are fixed high-speed ports. They do not support lower-speed connections (e.g., 10G) without expensive breakout cables or different transceivers, and changing speeds later would likely require physical re-cabling, which could disrupt adjacent ports in a dense chassis.
Reference:
FortiGate 6000F Hardware Guide – Network Interfaces:
SFP28 ports (1–24) can be configured for 1G, 10G, or 25G speeds via CLI commands (set speed). This allows speed adjustments to match upgraded switch ports without hardware replacement. QSFP28 ports (25–28) are fixed 40/100G and lack the same multi-speed flexibility for gradual migration.
Refer to the exhibit.
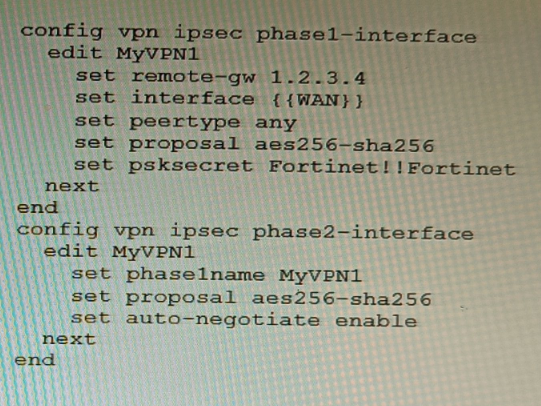
FortiManager is configured with the Jinja Script under CLI Templates shown in the exhibit.
Which two statements correctly describe the expected behavior when running this
template? (Choose two.)
A. The Jinja template will automatically map the interface with "WAN" role on the managed FortiGate.
B. The template will work if you change the variable format to $(WAN).
C. The template will work if you change the variable format to {{ WAN }}.
D. The administrator must first manually map the interface for each device with a meta field.
E. The template will fail because this configuration can only be applied with a CLI or TCL script.
🔍 Explanation:
FortiManager CLI templates using Jinja require variables to be enclosed in {{ }}. These variables must be mapped to per-device values using meta fields under Device Manager. This allows dynamic rendering of interface names or other parameters during template execution, ensuring device-specific configurations are correctly applied.
✅ Correct Option:
C. The template will work if you change the variable format to {{ WAN }}.
Jinja syntax requires double curly braces for variable substitution. FortiManager CLI templates using Jinja must follow this format to correctly render device-specific values during deployment.
D. The administrator must first manually map the interface for each device with a meta field.
Jinja variables like {{ WAN }} must be mapped to actual interface names per device using FortiManager’s meta variables. Without this mapping, the template will fail to render correctly.
❌ Why Other Options Are Incorrect :
A. The Jinja template will automatically map the interface with "WAN" role on the managed FortiGate.
Jinja does not auto-discover or auto-map interface roles. It relies on explicit variable mapping via meta fields. FortiManager does not infer that {{ WAN }} means the interface with role “WAN.” The administrator must manually define what WAN means for each device.
**B. The template will work if you change the variable format to
(
𝑊
𝐴
𝑁
)
.
∗
∗
‘
(WAN)is not valid Jinja syntax. That format is used in TCL or shell scripting, not in FortiManager’s Jinja-based CLI templates. Using$(WAN)` will result in a syntax error or failed rendering during template execution.
E. The template will fail because this configuration can only be applied with a CLI or TCL script.
FortiManager fully supports Jinja-based CLI templates starting from version 7.0.1+. The configuration shown (IPsec VPN setup) is valid and supported through Jinja templates. This option is incorrect because Jinja is explicitly designed for CLI template automation in FortiManager.
📚 Reference:
Fortinet KB Article:
New Meta Variables and Jinja Usage in FortiManager
| Page 3 out of 16 Pages |
| NSE8_812 Practice Test Home | Previous |
Choosing the right preparation material is critical for passing the Fortinet Network Security Expert 8 Written exam. Here’s how our NSE8_812 practice test is designed to bridge the gap between knowledge and a passing score.