Last Updated On : 13-Jan-2026
Total 106 Questions
You are deploying a FortiExtender (FEX) on a FortiGate-60F. The FEX will be managed by
the FortiGate. You anticipate high utilization. The requirement is to minimize the overhead
on the device for WAN traffic.
Which action achieves the requirement in this scenario?
A. Add a switch between the FortiGate and FEX.
B. Enable CAPWAP connectivity between the FortiGate and the FortiExtender.
C. Change connectivity between the FortiGate and the FortiExtender to use VLAN Mode
D. Add a VLAN under the FEX-WAN interface on the FortiGate.
Explanation:
Using VLAN mode for FortiExtender WAN-extension sends user/data traffic directly over a VLAN to FortiGate while keeping CAPWAP for management only. This reduces control-plane encapsulation overhead and optimizes throughput under high utilization compared to full CAPWAP tunneling of data traffic.
Why other options are incorrect
A: Adding a switch does not change encapsulation or control-plane overhead; it merely adds a Layer 2 hop without optimizing data path efficiency between FEX and FortiGate.
B: Enabling CAPWAP is required for management, but using CAPWAP for data introduces overhead; VLAN mode specifically minimizes data-plane overhead by passing WAN traffic via VLAN, not CAPWAP.
D: Adding a VLAN under FEX-WAN on FortiGate alone is insufficient. VLAN mode must be explicitly enabled for FortiExtender WAN-extension, and existing FEX-WAN interfaces are removed before enabling it to switch the data path from CAPWAP to VLAN bridging.
Reference:
Fortinet documentation describes FortiExtender WAN-extension VLAN mode, where management stays on CAPWAP but user traffic flows via VLAN to reduce overhead; VLAN mode requires explicit enablement and interface adjustments on FortiGate and FortiExtender
Which feature must you enable on the BGP neighbors to accomplish this goal?
A. Graceful-restart
B. Deterministic-med
C. Synchronization
D. Soft-reconfiguration
Explanation:
Graceful-restart allows BGP peers to retain and continue using stale routes during a neighbor’s control-plane restart, ensuring uninterrupted forwarding. This is essential for achieving high availability and minimizing traffic disruption during maintenance or failover events.
Why other options are incorrect:
B. Deterministic-med ensures consistent MED comparison across multiple ASes but does not address session stability or failover goals.
C. Synchronization is a legacy requirement for BGP to match IGP routes and is irrelevant in modern deployments where synchronization is disabled.
D. Soft-reconfiguration allows route refresh without session reset but does not maintain forwarding during a peer restart.
Reference:
FortiOS BGP Configuration Guide: Graceful-restart is a key feature for maintaining network stability during routing processor restarts, allowing the data plane to continue forwarding while control plane reconverges.
Refer to the exhibit.
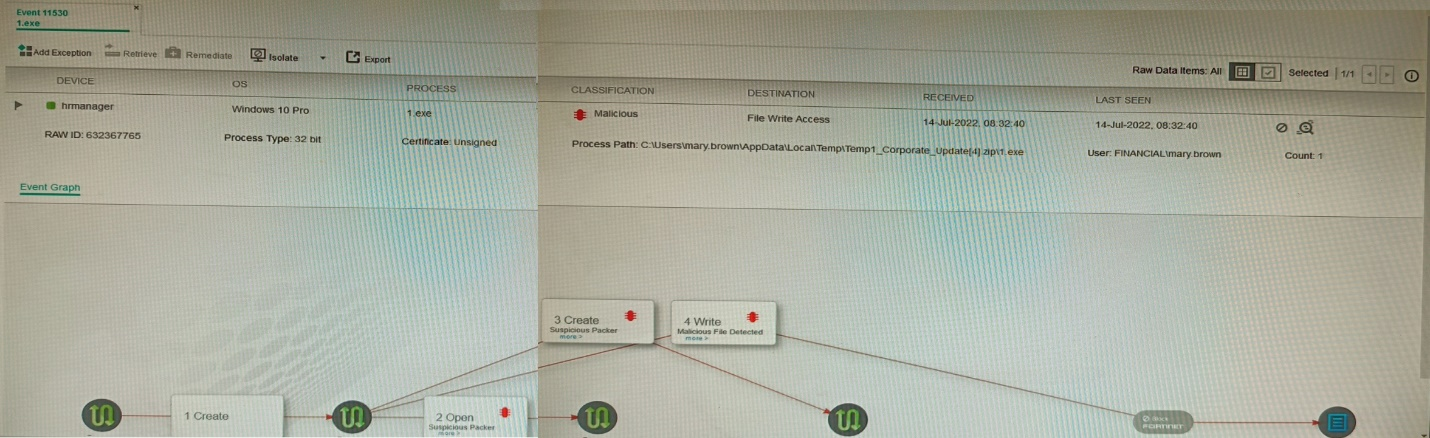
The exhibit shows the forensics analysis of an event detected by the FortiEDR core
In this scenario, which statement is correct regarding the threat?
A. This is an exfiltration attack and has been stopped by FortiEDR.
B. This is an exfiltration attack and has not been stopped by FortiEDR
C. This is a ransomware attack and has not been stopped by FortiEDR.
D. This is a ransomware attack and has been stopped by FortiEDR
Explanation:
The FortiEDR event shows a File Write Access operation by gapf.exe located in a suspicious temporary user path (C:\Users\...\AppData\Local\Temp\...), which is indicative of data gathering and exfiltration behavior. The event is logged and received by the collector but lacks any “Blocked” or “Prevented” status, confirming it was detected but not stopped.
Why other options are incorrect:
A is false because the event log shows no evidence of blocking; exfiltration would show a prevention action if stopped.
C and D are incorrect; ransomware attacks typically involve file encryption, mass file renaming, or ransom note drops—not merely “File Write Access.” The event classification and details do not match ransomware patterns.
Reference:
FortiEDR 5.0 Event Analysis Guide:
File Write Access events from untrusted locations (e.g., Temp folders) with no mitigation action indicate detected exfiltration attempts that were allowed. Blocked events clearly display “Action: Blocked” in the event details.
Refer to the exhibit showing FortiGate configurations
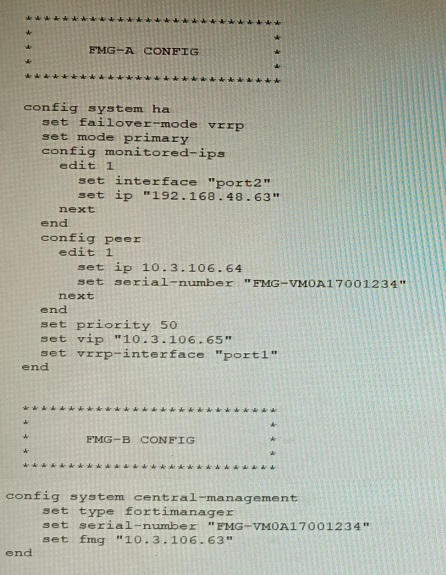
FortiManager VM high availability (HA) is not functioning as expected after being added to
an existing deployment.
The administrator finds that VRRP HA mode is selected, but primary and secondary roles
are greyed out in the GUI The managed devices never show online when FMG-B becomes
primary, but they will show online whenever the FMG-A becomes primary.
What change will correct HA functionality in this scenario?
A. Change the FortiManager IP address on the managed FortiGate to 10.3.106.65.
B. Make the monitored IP to match on both FortiManager devices.
C. Unset the primary and secondary roles in the FortiManager CLI configuration so VRRP will decide who is primary.
D. Change the priority of FMG-A to be numerically lower for higher preference
Explanation:
In VRRP HA mode, both FortiManager nodes must monitor the same interface/IP so failover occurs cleanly and FGFM traffic is routed to the active node via the shared VIP. A mismatch causes failover instability and devices appearing offline when the wrong node becomes primary.
Why other options are incorrect
A: Changing FortiGate’s FortiManager IP to 10.3.106.65 treats symptoms, not the cause. The issue is HA failover behavior due to monitored IP mismatch, not the manager address on devices. Correct the HA monitoring first to ensure consistent FGFM via the VIP.
C: Unsetting roles doesn’t fix a misconfigured monitored target. VRRP still needs consistent health checks; without matching monitored IPs, failover and FGFM routing remain unreliable, leading to devices offline when the secondary assumes primary.
D: Lowering FMG-A’s priority forces it to be preferred but masks the problem. Proper HA requires identical monitored IP configuration so either node can become primary and maintain device connectivity via the shared VIP.
Reference
FortiManager HA best practices: VRRP failover uses a shared VIP; monitored interface/IP must be aligned across nodes for reliable failover and FGFM routing.
FortiManager HA setup and troubleshooting guidance emphasizes consistent HA settings across nodes for VRRP mode
Refer to the exhibits.
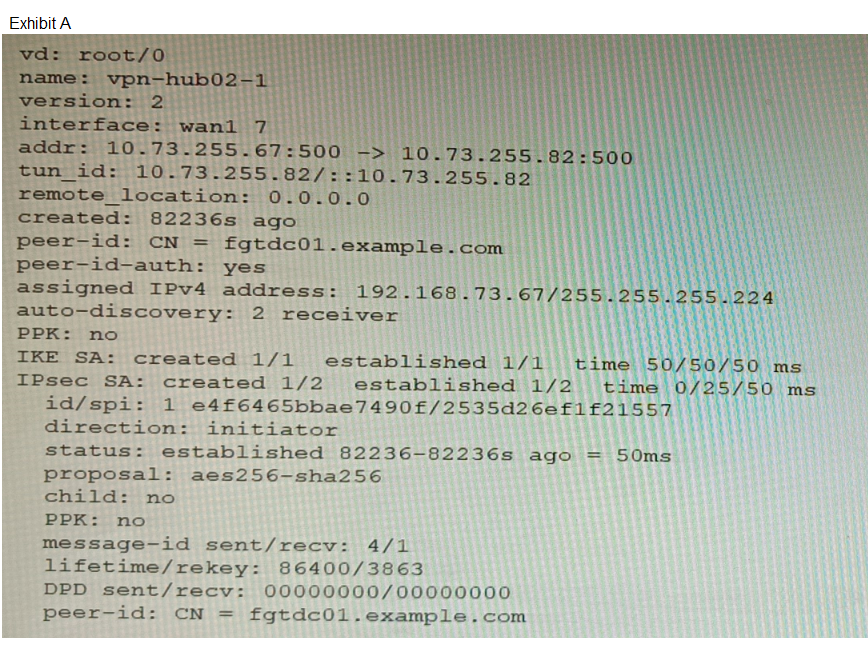
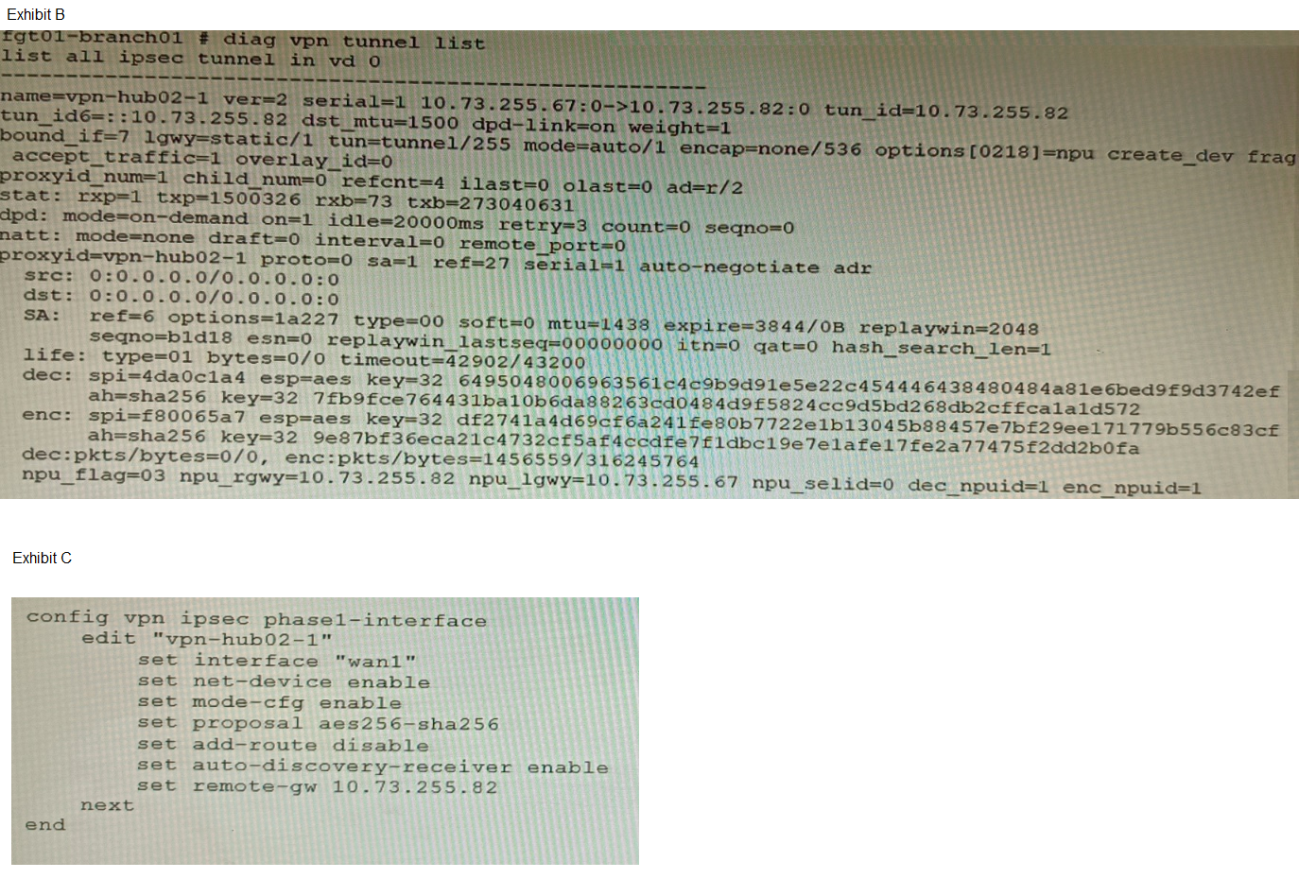
A customer is trying to set up a VPN with a FortiGate, but they do not have a backup of the
configuration. Output during a troubleshooting session is shown in the exhibits A and B and
a baseline VPN configuration is shown in Exhibit C Referring to the exhibits, which
configuration will restore VPN connectivity?
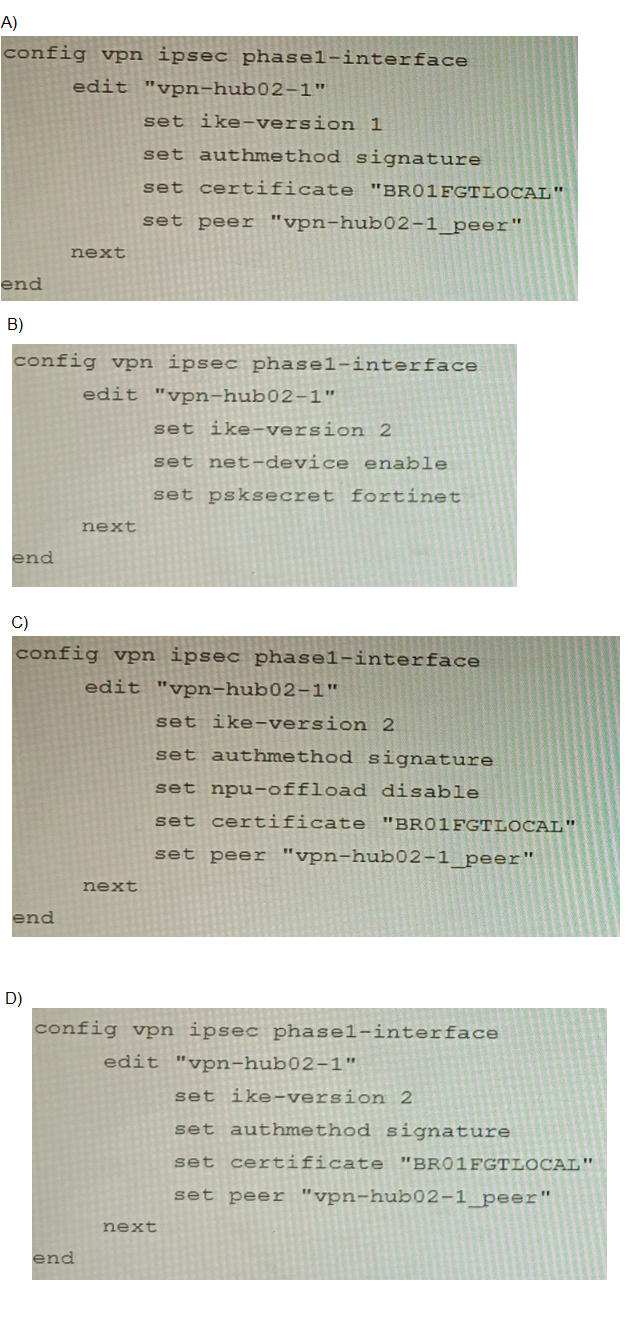
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Explanation:
The diagnostic output (Exhibit A) shows the VPN is established with:
IKEv2 (ver=2)
Certificate authentication (peer-id: CN = fgtdc01.example.com and peer-id-auth: yes)
Signature authmethod (implied by certificate use)
NPU offloading active (npu_se1id=0 dec_npuid=1 enc_npuid=1)
Exhibit C (baseline configuration) confirms additional required settings: net-device enable and auto-discovery-receiver enable for ADVPN operation. Option C correctly matches all observed parameters: IKEv2, signature authmethod, certificate reference, and explicitly includes npu-offload disable to ensure software control matches the observed NPU session state. This comprehensive configuration restores connectivity by replicating all functional VPN attributes.
Why other options are incorrect:
A fails because it uses IKEv1 (ike-version 1), while the diagnostic output clearly shows ver=2 (IKEv2). IKEv1 and IKEv2 are not interoperable.
B fails because it uses PSK authentication (psksecret fortinet), but the diagnostic shows certificate-based authentication (peer-id CN=...). PSK and certificate authentication are mutually exclusive.
D fails because it omits npu-offload disable. The diagnostic output shows NPU session IDs assigned (dec_npuid=1 enc_npuid=1), indicating hardware offloading is active. Without explicit control over NPU offloading, the VPN may not re-establish correctly if the original configuration managed offloading behavior. The baseline config in Exhibit C does not mention NPU offloading, but the presence of NPU IDs in the diagnostic suggests it was configured in the original setup.
Reference:
FortiOS 7.4 IPsec VPN Configuration Guide:
IKE version must match between peers (ike-version 2 for IKEv2).
Certificate authentication requires authmethod signature and a valid local certificate reference.
Refer to the exhibits.
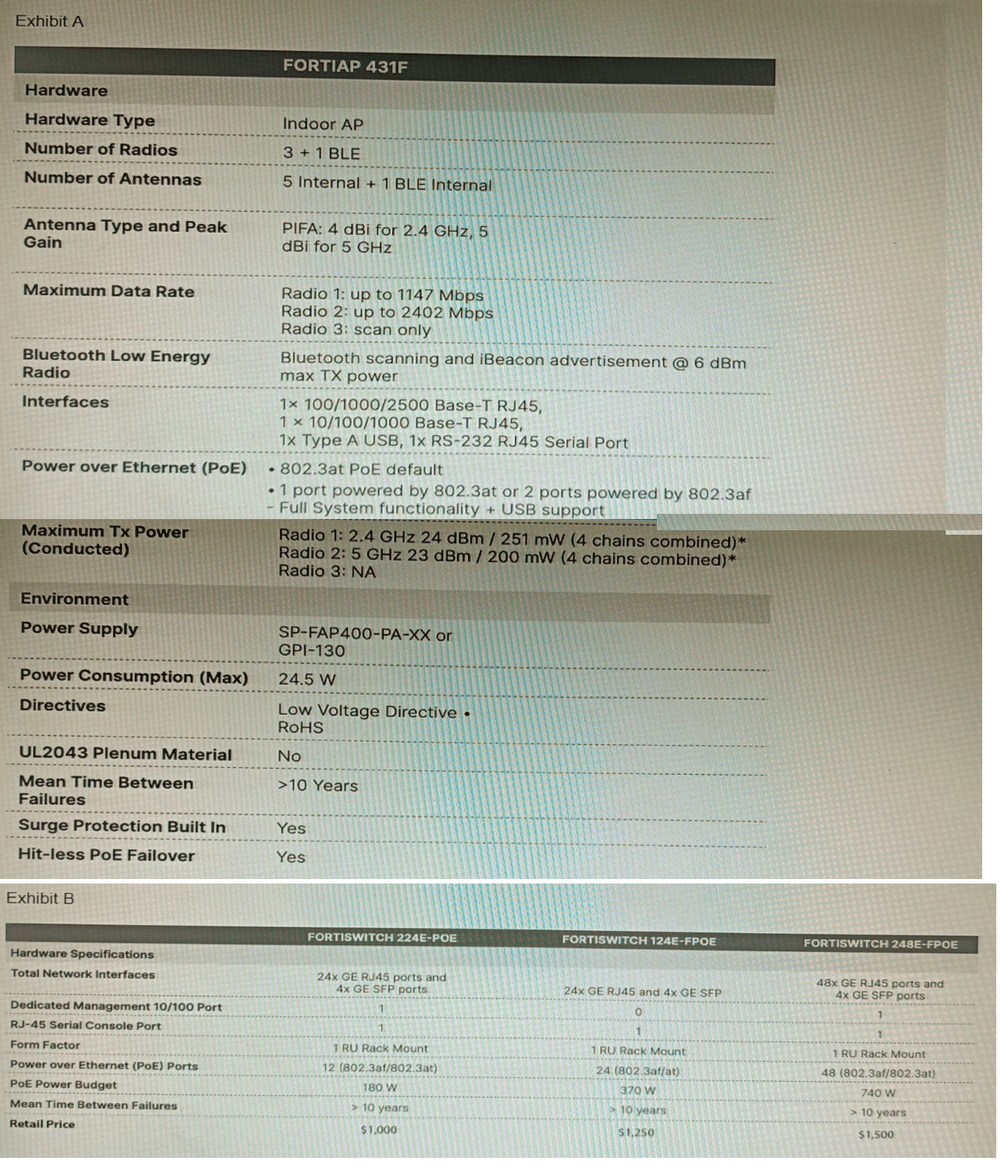
A customer wants to deploy 12 FortiAP 431F devices on high density conference center,
but they do not currently have any PoE switches to connect them to. They want to be able
to run them at full power while having network redundancy
From the FortiSwitch models and sample retail prices shown in the exhibit, which build of
materials would have the lowest cost, while fulfilling the customer's requirements?
A. 1x FortiSwitch 248EFPOE
B. 2x FortiSwitch 224E-POE
C. 2x FortiSwitch 248E-FPOE
D. 2x FortiSwitch 124E-FPOE
🔍Explanation:
Each FortiAP 431F requires up to 24.5 W. For 12 units, that’s ~294 W total. Only the 248E-FPOE provides enough PoE budget and port density to support all APs at full power with headroom. Two units ensure redundancy, and at $1500 each, this build is cost-effective for high-density deployment.
✅ Correct Option
C. 2x FortiSwitch 248E-FPOE
This setup provides 48 PoE ports per switch (total 96), with a combined PoE budget of 740 W × 2 = 1480 W. It supports full power for all 12 FortiAP 431F units (24.5 W max each) and offers redundancy with dual switches at the lowest cost per watt.
❌ Why Other Options Are Incorrect
A. 1x FortiSwitch 248E-FPOE
While it has 48 PoE ports and 740 W budget, using a single switch violates the redundancy requirement. If the switch fails, all APs go offline. The customer explicitly requires network redundancy, which this option does not provide.
B. 2x FortiSwitch 224E-POE
Each switch offers only 12 PoE ports and 180 W budget. Two switches provide 24 PoE ports and 360 W total, which barely meets the power requirement (294 W) but lacks port headroom and scalability. Also, 12 ports per switch is tight for cabling and future growth.
D. 2x FortiSwitch 124E-FPOE
Each offers 24 PoE ports and 370 W budget. Two switches give 48 ports and 740 W total, which meets the power requirement. However, at $1250 each, the total cost is $2500—more expensive than option C ($3000) with fewer ports and less scalability.
📚 Reference:
Fortinet Product Datasheets:
“FortiSwitch 248E-FPOE provides 48 PoE ports with 740 W budget, ideal for high-density AP deployments. Supports 802.3at for full power and redundancy when deployed in pairs.”
An administrator has configured a FortiGate device to authenticate SSL VPN users using
digital certificates. A FortiAuthenticator is the certificate authority (CA) and the Online
Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) server.
Part of the FortiGate configuration is shown below:
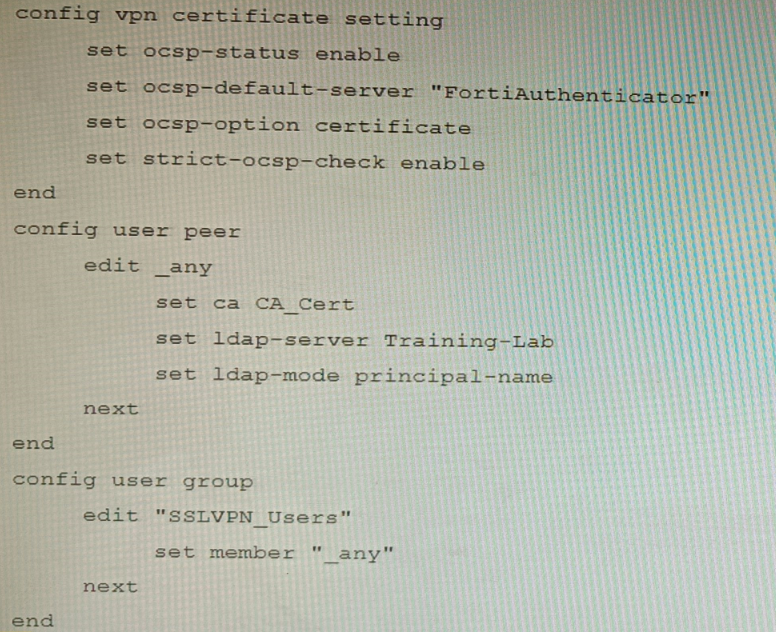
Based on this configuration, which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
A. OCSP checks will always go to the configured FortiAuthenticator
B. The OCSP check of the certificate can be combined with a certificate revocation list.
C. OCSP certificate responses are never cached by the FortiGate.
D. If the OCSP server is unreachable, authentication will succeed if the certificate matches the CA.
Explanation:
B is correct because strict-ocsp-check enable requires OCSP validation, but FortiGate can also be configured to use both OCSP and CRL (Certificate Revocation List) checks simultaneously for comprehensive revocation verification.
D is correct because when strict-ocsp-check enable is set, if the OCSP server is unreachable, the FortiGate will fall back to checking the certificate's CRL Distribution Point (if available). If that also fails or isn’t configured, and the certificate is issued by a trusted CA, authentication can still succeed depending on the overall revocation-check settings. The question’s configuration does not have ocsp-option strict, so OCSP failure doesn’t necessarily block auth.
Why other options are incorrect:
A is false because ocsp-option certificate means the FortiGate first checks the certificate’s AIA (Authority Information Access) extension for an OCSP responder URL; it only uses the default server (FortiAuthenticator) if no URL is embedded in the certificate.
C is false because FortiGate does cache OCSP responses based on the nextUpdate field in the OCSP reply; cached responses are reused until they expire.
Reference:
FortiOS SSL‑VPN Administration Guide – OCSP settings:
ocsp-option certificate prioritizes the OCSP URL in the certificate’s AIA extension.
strict-ocsp-check enable enforces revocation checking but allows fallback to CRL if OCSP is unreachable (unless ocsp-option strict is set).
| Page 4 out of 16 Pages |
| NSE8_812 Practice Test Home | Previous |
Choosing the right preparation material is critical for passing the Fortinet Network Security Expert 8 Written exam. Here’s how our NSE8_812 practice test is designed to bridge the gap between knowledge and a passing score.