Last Updated On : 13-Jan-2026
Total 50 Questions
When configuring firewall policies which of the following is true regarding the policy ID? (Choose two.)
A. A firewall policy ID identifies the order of policy execution in firewall policies.
B. A policy ID cannot be modified once a policy is created.
C. You can create a policy in CLI with policy ID 0
D. It is mandatory to provide a policy ID while creating a firewall policy regardless of GUI or CLI.
Explanation:
Correct answers: A and B
A. A firewall policy ID identifies the order of policy execution in firewall policies.
Correct.
FortiGate evaluates firewall policies top-down by policy ID order. The policy with the lowest ID is evaluated first, then the next higher ID, and so on, until a match is found.
This is why policy reordering in the GUI actually changes policy IDs under the hood.
Important nuance:
The GUI hides this detail by letting you drag policies, but internally FortiOS still uses policy IDs to define execution order.
B. A policy ID cannot be modified once a policy is created.
Correct.
Once a policy is created, its policy ID is immutable. You cannot edit it directly in either GUI or CLI.
To change order, FortiGate:
Renumbers policy IDs automatically (GUI move), or
Requires deleting and recreating the policy (CLI, if you want a specific ID)
This is a common exam trap. You can move policies, but you cannot manually change an existing policy’s ID.
Why the other options are wrong
C. You can create a policy in CLI with policy ID 0
Incorrect.
Policy ID 0 is reserved and cannot be used for user-defined firewall policies. Attempting this in CLI will fail.
Valid policy IDs start from 1.
D. It is mandatory to provide a policy ID while creating a firewall policy regardless of GUI or CLI.
Incorrect.
GUI: You never specify a policy ID. FortiGate assigns it automatically.
CLI: If you use edit 0, FortiGate auto-assigns the next available ID.
config firewall policy
edit 0
set name "example"
next
end
The system assigns the ID for you.
Reference:
FortiOS 7.6 Administration Guide → Firewall Policy Order and Matching
An administrator has configured a dialup IPsec VPN on FortiGate with add-route enabled. However, the static route is not showing in the routing table. Which two statements about this scenario are correct? (Choose two.)
A. The administrator must use a policy route instead of a static route for add-route to work properly.
B. The administrator must ensure phase 2 is successfully established
C. The administrator must define the remote network correctly in the phase 2 selectors.
D. The administrator must enable a dynamic routing protocol on the dialup interface.
Explanation:
B. The administrator must ensure phase 2 is successfully established The add-route feature in FortiOS is event-driven. The FortiGate does not pre-populate the routing table when the tunnel is configured; instead, it waits for a successful Phase 2 (IPsec SA) negotiation. Only after the Phase 2 selectors are negotiated and the security association is active will the FortiGate "install" the corresponding route into the routing table. If the tunnel is down or only Phase 1 is up, the route will not appear.
C. The administrator must define the remote network correctly in the phase 2 selectors The add-route feature specifically uses the Phase 2 Quick Mode selectors (specifically the "Remote Address" or "Proxy-ID") to determine what destination to add to the routing table.
🔹 If the remote client proposes a subnet (e.g., 10.0.1.0/24), the FortiGate uses that information to create a static route pointing to the tunnel.
🔹 If the Phase 2 selectors are set to 0.0.0.0/0 (all traffic) or are incorrectly defined, the FortiGate may not have a specific enough prefix to install, or it may conflict with existing routes.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A: Policy routes are used to bypass the routing table for specific traffic steering. add-route is specifically designed to populate the RIB (Routing Information Base) with static routes; you do not need a policy route to make the static route appear.
D: While dynamic routing protocols (like BGP or OSPF) are common in large-scale VPN deployments (like ADVPN), the add-route feature is a static/manual alternative to dynamic routing. Enabling a dynamic protocol is a different method entirely and is not a requirement for the add-route setting to function.
Reference
FortiOS 7.6 Administration Guide: "When add-route is enabled on a dialup server, the FortiGate unit adds a host route to its routing table for each dialup client that connects. The route is added when the Phase 2 SA is established and uses the remote IP address from the Phase 2 selector."
Refer to the exhibit.
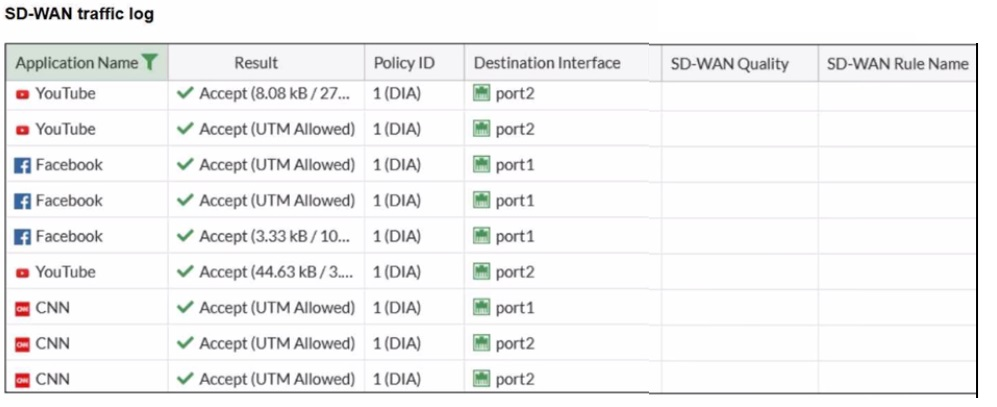
The administrator configured SD-WAN rules and set the FortiGate traffic log page to
display SD-WAN-specific columns: SD-WAN Quality and SD-WAN Rule Name
FortiGate allows the traffic according to policy ID 1 placed at the top. This is the policy that
allows SD-WAN traffic. Despite these settings, the traffic logs do not show the name of the
SD-WAN rule used to steer those traffic flows
What could be the reason?
A. SD-WAN rule names do not appear immediately. The administrator must refresh the page.
B. There is no application control profile applied to the firewall policy.
C. Destinations in the SD-WAN rules are configured for each application, but feature visibility is not enabled.
D. FortiGate load balanced the traffic according to the implicit SD-WAN rule.
Explanation:
The correct answer is D. FortiGate load balanced the traffic according to the implicit SD-WAN rule.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of why this is the case and why the other options are less likely:
Detailed Explanation:
✔️ How SD-WAN Rules Work: An SD-WAN rule is a matching condition that tells the FortiGate how to handle specific traffic (e.g., route "YouTube" traffic to port2). The SD-WAN Rule Name column in the log will only show a value if traffic was matched and steered by a user-defined SD-WAN rule that you configured.
✔️ The Implicit SD-WAN Rule: At the bottom of the SD-WAN rule list, there is always an implicit (default) SD-WAN rule. Its purpose is to catch any traffic that does not match any of the user-defined rules above it. This implicit rule performs automatic load balancing based on the link health and load-balancing algorithm. Crucially, when traffic is handled by this implicit rule, the SD-WAN Rule Name field in the logs remains blank.
✔️ Analyzing the Logs: Your logs show "YouTube" traffic consistently going to port2 and "Facebook" to port1. While this looks like steering, without a specific rule name, it is the result of the implicit rule's load-balancing decision. The traffic for "CNN" is split between port1 and port2, which is classic behavior of a load-balancing rule, not a specific performance rule tied to a named application.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Refresh the page
Rule names appear in logs immediately if a rule is matched. A refresh is not needed.
B. No application control profile
Application control identifies the apps (YouTube, Facebook), which is already working as seen in the Application Name column. This is not related to SD-WAN rule naming.
C. Feature visibility not enabled
The SD-WAN Quality and SD-WAN Rule Name columns are already visible in the log viewer, meaning feature visibility is enabled. The issue is that the column is empty, not missing.
Key Takeaway for the Exam:
A blank SD-WAN Rule Name in the traffic log, while all other SD-WAN information is present, is the primary indicator that traffic is being handled by the implicit SD-WAN rule for load balancing.
Refer to the exhibit.
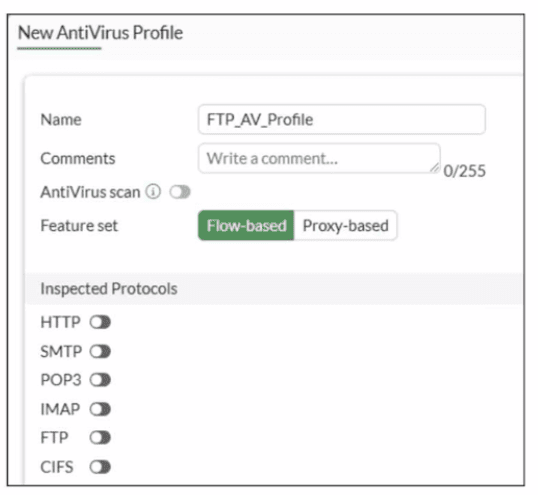
Why is the Antivirus scan switch grayed out when you are creating a new antivirus profile
for FTP?
A. Antivirus scan is disabled under System -> Feature visibility
B. None of the inspected protocols are active in this profile.
C. The Feature Set for the profile is Flow-based but it must be Proxy-based
D. FortiGate. with less than 2 GB RAM. does not support the Antivirus scan feature.
Explanation:
✅ Correct Answer: B
The Antivirus scan switch is grayed out because no inspected protocols are selected in the FTP Antivirus profile. In FortiGate, the Antivirus scan option becomes available only after enabling at least one protocol (such as FTP) under Inspected Protocols, as antivirus scanning requires a protocol context to operate.
The exhibit shows FTP unchecked along with all other protocols (HTTP, SMTP, IMAP, POP3, CIFS), leaving no scanning scope defined, which disables the feature toggle.
❌ Why others are wrong:
A: Feature visibility affects global UI options but doesn't gray out per-profile settings like this.
C: Flow-based supports FTP AV scanning; Proxy-based isn't required for basic antivirus on FTP traffic.
D: RAM size doesn't disable AV scan availability; it's a configuration prerequisite issue.
Reference:
FortiOS 7.6 Administration Guide - Antivirus Profile configuration (Content Inspection section, NSE4_FGT_AD-7.6 exam topics).
A network administrator is reviewing firewall policies in both Interface Pair View and By Sequence View. The policies appear in a different order in each view. Why is the policy order different in these two views?
A. By Sequence View groups policies based on rule priority, while Interface Pair View always follows the order of traffic logs.
B. The firewall dynamically reorders policies in Interface Pair View based on recent traffic patterns, but By Sequence View remains static.
C. Interface Pair View sorts policies based on matching interfaces, while By Sequence View shows the actual processing order of rules.
D. Policies in Interface Pair View are prioritized by security levels, while By Sequence View strictly follows the administrator's manual ordering.
Explanation:
The correct answer is C. Interface Pair View sorts policies based on matching interfaces, while By Sequence View shows the actual processing order of rules.
Here's why the orders look different:
FortiGate evaluates firewall policies top-down in a single, fixed sequence—the order you see in By Sequence View. That's the real processing order: the first matching policy wins, full stop. This view lists every policy exactly as it's checked, without any grouping.
Interface Pair View organizes the same policies into collapsible sections/groups based on the incoming and outgoing interface pairs (e.g., all policies from port1 → port2 in one section, port2 → wan1 in another). Within each section, the relative order matches the global sequence, but because it's grouped by interface pairs, the overall list appears reordered compared to the flat By Sequence View. It's just a different way to display the same set of rules for easier management when you have many policies—especially useful when troubleshooting traffic between specific interfaces.
The key point: both views reflect the same evaluation logic and order; only the presentation changes. Interface Pair View doesn't change priorities or reorder anything—it groups by src/dst interfaces to make scanning faster.
Why the others don't hold up:
A — No, neither view bases order on traffic logs, and rule priority isn't a separate thing here (it's the sequence).
B — FortiGate doesn't dynamically reorder policies based on traffic patterns in any view. The order is static unless you manually move rules.
D — There's no prioritization by "security levels" in Interface Pair View (that's not a FortiGate concept for policy ordering). By Sequence does follow the admin's manual ordering, but that's true for both—the difference is grouping, not priority method.
This is straight from Fortinet's docs (FortiOS 7.6 Administration Guide, Firewall Policy section, and the Policy views/policy lookup topic): Interface Pair View groups by incoming/outgoing pairs while showing check order within groups; By Sequence is the ungrouped, full top-down list.
Refer to the exhibits.
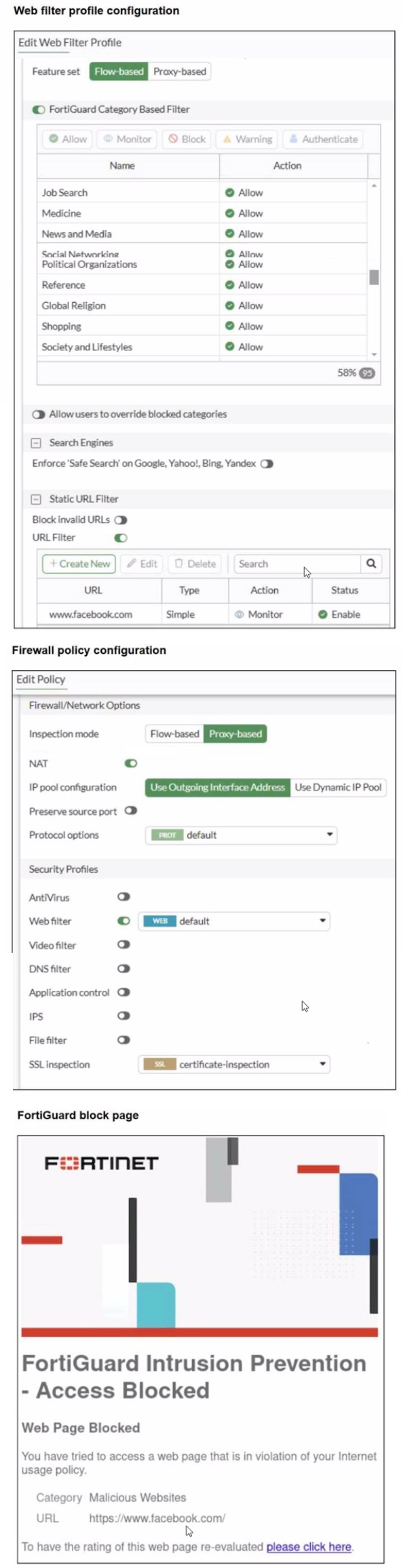
A web filter profile configuration and firewall policy configuration are shown.
You are trying to access www. facebook.com, but you are redirected to a FortiGuard web
filtering block page.
Based on the exhibits, what is the possible cause of the issue?
A. The web rating override configuration is incorrect.
B. The web filter profile feature set is configured incorrectly.
C. The firewall policy inspection mode is incorrect.
D. For www. facebook. com. the URL filter action is incorrect.
Explanation:
Correct answer: B
What is happening (read the exhibits carefully)
🔹 The web filter profile is configured as Flow-based.
🔹 The firewall policy inspection mode is Proxy-based.
🔹 Accessing www.facebook.com results in a FortiGuard web filtering block page, categorized as Malicious Websites.
🔹 The URL filter entry for www.facebook.com is set to Monitor, not Block.
This mismatch is the key.
Why B is correct
B. The web filter profile feature set is configured incorrectly.
You are mixing flow-based security profiles with a proxy-based firewall policy.
In FortiOS:
🔹 Proxy-based inspection mode requires proxy-based security profiles
🔹 Flow-based profiles are not fully compatible with proxy mode
When this mismatch exists, FortiGate behavior becomes inconsistent. Web filtering decisions can fall back to FortiGuard category enforcement without correctly honoring URL filter actions like Monitor.
That explains why:
🔹 Facebook is being blocked
🔹 Even though its URL filter action is Monitor
🔹 And category list shows Social Networking allowed
This is a classic NSE4 exam scenario: profile type mismatch causes unexpected blocking.
Why the other options are wrong
A. The web rating override configuration is incorrect.
Incorrect.
There is no exhibit showing any web rating override configuration. Also, rating overrides are explicit entries and would be visible in the profile. This is a distraction option.
C. The firewall policy inspection mode is incorrect.
Incorrect.
Proxy-based inspection mode is valid and required for:
🔹 Web filtering
🔹 Certificate inspection
🔹 Advanced HTTP inspection features
The issue is not proxy mode itself, but that it is paired with a flow-based profile.
D. For www.facebook.com, the URL filter action is incorrect.
Incorrect.
The URL filter entry for www.facebook.com is:
🔹 Action: Monitor
🔹 Status: Enabled
Monitor does not block traffic. If this were the cause, the site would load and only be logged. The block page proves the decision is happening elsewhere.
Core rule you must remember for NSE4
Flow-based profiles must be used with flow-based inspection.
Proxy-based inspection requires proxy-based profiles.
Mixing them leads to:
🔹 Unexpected blocks
🔹 Category overrides not behaving correctly
🔹 URL filter actions ignored
Fortinet reference (official)
FortiOS 7.6 Administration Guide
🔹 Web Filter Profiles
🔹 Proxy-based vs Flow-based Inspection
Fortinet explicitly states that security profile feature sets must match the policy inspection mode
Which statement correctly describes NetAPI polling mode for the FSSO collector agent?
A. The collector agent uses a Windows API to query DCs for user logins.
B. The NetSessionEnum function is used to track user logouts.
C. NetAPI polling can increase bandwidth usage in large networks.
D. The collector agent must search Windows application event logs.
Explanation:
The correct statement describing the NetAPI polling mode for the FSSO collector agent is:
✅ B. The NetSessionEnum function is used to track user logouts.
Technical Explanation
The NetAPI polling mode is one of three collector-agent-based polling methods (the others being WinSecLog and WMI). Here is how it operates:
Mechanism: The Collector Agent periodically connects to the Domain Controllers (typically every 9 seconds) and calls the Windows NetSessionEnum function.
Tracking Logons/Logouts: This function retrieves a list of all active sessions currently established on the DC. By comparing the results of the current poll to the previous one, the collector agent can identify:
Logons: New sessions that appear in the list.
Logouts: Sessions that were present in the previous poll but are now missing from the list.
Pros and Cons: It is the fastest polling method because it queries RAM rather than parsing large log files. However, it can miss logon events if a user logs in and then logs out quickly between two 9-second polling intervals.
Why the Other Options are Incorrect
❌ A: The collector agent uses a Windows API to query DCs for user logins. While technically true that it uses an API, this statement is considered too "generic" for the exam. The exam specifically looks for the function name (NetSessionEnum) or the specific behavior of how it manages sessions (both login and logout).
❌ C: NetAPI polling can increase bandwidth usage in large networks. This is a characteristic of WinSecLog polling, not NetAPI. WinSecLog requires the collector agent to pull and parse large security event logs from the DCs, which consumes significantly more bandwidth than the lightweight NetAPI session query.
❌ D: The collector agent must search Windows application event logs. This is incorrect. NetAPI queries the active session table in RAM. Searching logs is the method used by WinSecLog (Security Event Logs) or WMI.
Reference
FortiOS 7.6 Study Guide - FSSO: "NetAPI: Polls temporary sessions created on the DC when a user logs in or logs out and calls the NetSessionEnum function on Windows. It is faster than WinSec and WMI methods but can miss logon events under heavy load."
| Page 2 out of 8 Pages |
| NSE4_FGT_AD-7.6 Practice Test Home |
Choosing the right preparation material is critical for passing the Fortinet NSE 4 - FortiOS 7.6 Administrator exam. Here’s how our NSE4_FGT_AD-7.6 practice test is designed to bridge the gap between knowledge and a passing score.