Last Updated On : 3-Mar-2026
Total 55 Questions
The smartest way to prepare for your Fortinet NSE4_FGT_AD-7.6 exam isn't just reading—it's practicing. Our Fortinet NSE 4 FortiOS 7.6 Administrator practice test bridge gap, transforming your knowledge into a passing score. Familiarize yourself with the exact style and difficulty of the real Fortinet NSE4_FGT_AD-7.6 practice questions, so there are no surprises. Get detailed feedback to identify your strengths and target your weaknesses, making your study time more efficient.
What are two features of FortiGate FSSO agentless polling mode? (Choose two.)
A. FortiGate uses the AD server as the collector agent.
B. FortiGate uses the SMB protocol to read the event viewer logs from the DCs.
C. FortiGate does not support workstation check.
D. FortiGate directs the collector agent to use a remote LDAP server.
Explanation:
Correct Answers: B and C
🟢 FortiGate FSSO agentless polling mode enables user authentication monitoring without deploying external DC or collector agents. FortiGate directly polls domain controllers using the SMB protocol over TCP port 445 to read Windows Security event logs (specifically event IDs 4768 and 4769 for logon/logoff), confirming option B.
🟢 Workstation check (verification of user IP-to-hostname binding) is not supported in agentless mode, as FortiGate lacks the additional capabilities of a dedicated collector agent, making option C correct.
🔴 Option A is incorrect because FortiGate itself acts as the collector, not the AD server.
🔴 Option D is wrong, as agentless polling does not involve directing a collector agent or remote LDAP for event collection; LDAP serves group filtering separately.
Reference: FortiGate 7.4 Administration Guide (FSSO Polling Connector) and NSE4 study materials covering FortiOS 7.6 FSSO topics.
You have configured the below commands on a FortiGate.

What would be the impact of this configuration on FortiGate?
A. FortiGate will enable strict RPF on all its interfaces and porti will be exempted from RPF checks.
B. FortiGate will enable strict RPF on all its interfaces and porti will be enable for asymmetric routing.
C. The global configuration will take precedence and FortiGate will enable strict RPF on all interfaces.
D. Port1 will be enabled with flexible RPF. and all other interfaces will be enabled for strict RPF
Explanation:
The correct answer is A. FortiGate will enable strict RPF on all its interfaces and port1 will be exempted from RPF checks.
Here's what this configuration actually does:
✔️ config system settings → set strict-src-check enable
This globally enables strict Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) mode for the VDOM.
In strict mode, FortiGate performs a stricter anti-spoofing check: for every incoming packet, it looks up the best route back to the source IP. If that best reverse route doesn't point out the same interface the packet came in on, the packet is dropped.
(By default, without this setting, it's feasible/loose mode, which only requires at least one feasible route back via the incoming interface.)
✔️ config system interface → edit port1 → set src-check disable
This disables the source/RPF check completely on port1 only.
So even though strict mode is active globally, port1 ignores the RPF check entirely—packets coming in on port1 won't be dropped for failing the reverse path check (useful for asymmetric routing scenarios or certain VPNs where return traffic takes a different path).
The per-interface src-check disable overrides the global strict-src-check setting for that specific interface. Strict mode applies to every other interface, but port1 is fully exempted from any RPF validation.
Why the others are incorrect:
B — "port1 will be enable for asymmetric routing" is vague and not precise. Disabling src-check on port1 does allow asymmetric traffic through that interface (since RPF won't block it), but the phrasing "enable for asymmetric routing" isn't how FortiGate describes it, and it doesn't match the full impact.
C — No, the interface-level setting takes precedence over the global one here. Global doesn't override per-interface disable.
D — "Flexible RPF" isn't a real term in FortiGate. The modes are strict vs feasible (loose). Disabling src-check isn't "flexible"—it's completely off for that interface.
Reference:
Fortinet's official documentation (e.g., FortiOS 7.6 Administration Guide → Routing concepts section) and the key technical tip on community.fortinet.com explain this behavior clearly:
🔹 strict-src-check enable → strict RPF globally
🔹 src-check disable on interface → bypasses RPF entirely on that interface, overriding the global mode
A network administrator has enabled full SSL inspection and web filtering on FortiGate. When visiting any HTTPS websites, the browser reports certificate warning errors. When visiting HTTP websites, the browser does not report errors. What is the reason for the certificate warning errors?
A. The option invalid SSL certificates is set to allow on the SSL/SSH inspection profile.
B. The matching firewall policy is set to proxy inspection mode.
C. The browser does not trust the certificate used by FortiGate for SSL inspection.
D. The certificate used by FortiGate for SSL inspection does not contain the required certificate extensions.
Explanation:
Why C is correct
With full SSL inspection, FortiGate performs a man-in-the-middle operation on HTTPS traffic. It resigns the server certificate using a local CA certificate configured in the SSL/SSH inspection profile.
If the client browser does not trust that CA, it cannot validate the certificate chain, so it throws a certificate warning.
This behavior only affects HTTPS because:
🔹 HTTPS uses certificates and trust chains.
🔹 HTTP does not use certificates at all, so no warning appears.
This is the classic and expected outcome when the FortiGate CA certificate has not been installed and trusted on the client.
Why the other options are wrong
A. The option invalid SSL certificates is set to allow on the SSL/SSH inspection profile.
Incorrect.
This setting controls how FortiGate handles upstream server certificates that are invalid (expired, self-signed, etc.). It does not affect whether the client trusts FortiGate’s own inspection certificate. Even if set to allow, the browser will still warn if it does not trust FortiGate’s CA.
B. The matching firewall policy is set to proxy inspection mode.
Incorrect.
Proxy mode is required for full SSL inspection and web filtering. It is not the cause of certificate warnings. If anything, proxy mode is functioning correctly here.
D. The certificate used by FortiGate for SSL inspection does not contain the required certificate extensions.
Incorrect.
FortiGate-generated CA certificates include the necessary extensions for SSL inspection by default. Missing extensions would indicate a broken or manually misconfigured certificate, which is not the standard cause tested in NSE4. The exam expects you to recognize the client trust issue, not certificate structure problems.
Key exam takeaway
Full SSL inspection always causes certificate warnings unless the FortiGate CA certificate is trusted by the client.
Reference (Fortinet official)
🔹 FortiOS Administration Guide – SSL/SSH Inspection
Explains that the FortiGate re-signs certificates and requires the CA certificate to be installed on client devices.
Fortinet Documentation → FortiOS 7.6 → Security Profiles → SSL/SSH Inspection
Refer to the exhibits.

An administrator has observed the performance status outputs on an HA cluster for 55
seconds.
Which FortiGate is the primary?
A. HQ-NGFW-1 with the parameter memory-failover-flip-timeout setting
B. HQ-NGFW-2 with the parameter priority setting
C. HQ-NGFW-1 with the parameter override setting
D. HQ-NGFW-2 with the parameter memory-failover-threshold setting
Explanation:
The correct answer is D.
Technical Analysis
In this scenario, we must evaluate the HA election criteria specifically for memory-based failover, which is a feature enabled in this cluster's configuration.
➡️ Memory Threshold Breach: The configuration for HQ-NGFW-1 sets a memory-failover-threshold of 70%. Performance status shows HQ-NGFW-1 is currently at 90% memory usage, while HQ-NGFW-2 is at approximately 48.7%.
➡️ Monitoring Period: The memory-failover-monitor-period is set to 50 seconds. This is the duration the memory must stay above the threshold to trigger a failover.
➡️ Observation Window: The administrator has observed these statuses for 55 seconds. Because 55 seconds is greater than the 50-second monitor period, the threshold violation has been sustained long enough to trigger a failover.
➡️ Resulting Primary: Once the primary (HQ-NGFW-1) triggers a failover due to memory pressure, the secondary unit with memory usage below the threshold (HQ-NGFW-2) becomes the new primary.
Why Other Options are Incorrect
A: The memory-failover-flip-timeout (set to 60 minutes in this case) is a timer that prevents the cluster from failing back to the original unit too quickly to avoid "flapping". It does not determine which unit is currently primary during the initial 55-second window.
B: While HQ-NGFW-2 has a priority setting, the memory-based failover event overrides standard priority-based election when one unit exceeds its healthy resource threshold for the defined period.
C: Even though HQ-NGFW-1 has a higher priority (200) and override might be disabled, the specific memory-failover trigger has already transitioned the role to HQ-NGFW-2.
Reference
FortiOS 7.6 Administration Guide: "When memory-based failover is enabled, a failover occurs if the primary unit's memory usage exceeds the memory-failover-threshold for a duration longer than the memory-failover-monitor-period."
What are two features of collector agent advanced mode? (Choose two.)
A. In advanced mode, security profiles can be applied only to user groups, not individual users.
B. In advanced mode. FortiGate can be configured as an LDAP client and group filters can be configured on FortiGate.
C. Advanced mode uses the Windows convention—NetBios: Domain\Username.
D. Advanced mode supports nested or inherited groups.
Explanation:
The two correct features of collector agent advanced mode are:
🔹 Advanced mode supports nested or inherited groups.
🔹 In advanced mode, FortiGate can be configured as an LDAP client and group filters can be configured on FortiGate.
The information is consistent across multiple exam preparation sites. The table below breaks down why each answer choice is correct or incorrect.
✅ Correct
A. Supports nested or inherited groups
This is a key feature of advanced mode, allowing it to recognize users in subgroups within monitored Active Directory groups.
B. FortiGate as LDAP client with group filters
In advanced mode, FortiGate can query LDAP/AD directly, and group filters are configured on the FortiGate itself for more granular control.
❌ Incorrect
C. Security profiles only for user groups
In both standard and advanced modes, security profiles can be applied to individual users or groups. This is not a distinguishing feature of advanced mode.
D. Uses Windows convention (NetBIOS)
This is actually a feature of standard mode. Advanced mode typically uses the LDAP naming convention (CN=User, OU=Name, DC=Domain).
✍️ Key Takeaway for the Exam
The main distinctions between standard and advanced mode often center on nested group support and where configuration occurs (agent vs. FortiGate). To solidify this, focus on understanding the operational differences in how user and group information is retrieved and processed in each mode.
Refer to the exhibit.
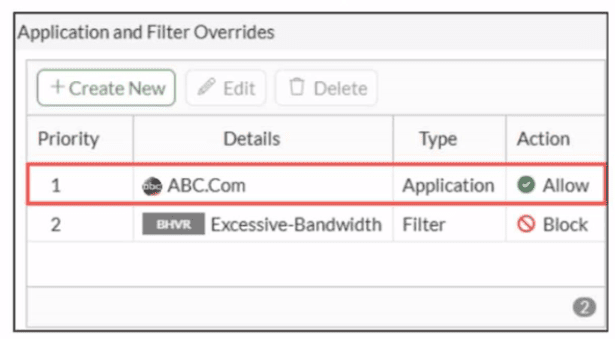
An administrator has configured an Application Overrides for the ABC.Com application
signature and set the Action to Allow This application control profile is then applied to a
firewall policy that is scanning all outbound traffic. Logging is enabled in the firewall policy.
To test the configuration, the administrator accessed the ABC.Com web site several times.
Why are there no logs generated under security logs for ABC.Com?
A. The ABC Com is hitting the category Excessive-Bandwidth.
B. The ABC.Com Type is set as Application instead of Filter.
C. The ABC.Com is configured under application profile, which must be configured as a web filter profile.
D. The ABC Com Action is set to Allow
Explanation:
Correct Answer: D
The ABC.Com application override is configured with Action set to Allow in the application control profile. In FortiGate, when an application override explicitly allows traffic (regardless of the base signature category or default action), no security log event is generated for that specific application because allowed override traffic bypasses standard logging mechanisms in application control.
The profile is correctly applied to a firewall policy scanning outbound traffic with logging enabled, but the explicit Allow override prevents ABC.Com detection from triggering a log entry under Log & Report > Security Events > Application Control.
Why others are wrong:
A: Incorrect. Excessive-Bandwidth is a separate filter override (priority 2, Block action) that doesn't affect ABC.Com (priority 1).
B: Incorrect. Application type is appropriate for custom application signatures like ABC.Com; Filter type is for category-based rules.
C: Incorrect. Application overrides belong in application control profiles, not web filter profiles.
Reference: FortiOS 7.6 Application Control documentation on override logging behavior and NSE4_FGT_AD-7.6 content inspection topics.
An administrator wants to form an HA cluster using the FGCP protocol. Which two requirements must the administrator ensure both members fulfill? (Choose two.)
A. They must have the same hard drive configuration.
B. They must have the same number of configured VDOMs.
C. They must have the heartbeat interfaces in the same subnet
D. They must have the same HA group ID.
Explanation:
The correct answers are C and D.
✔️ C. They must have the heartbeat interfaces in the same subnet
✔️ D. They must have the same HA group ID.
Here's the breakdown:
For FGCP HA to form a cluster successfully, the FortiGates must match on several key HA-specific settings so they can discover each other, negotiate, and synchronize properly via the heartbeat.
✅ Heartbeat interfaces in the same subnet (C):
The dedicated heartbeat interfaces (usually ha1/ha2 or whatever you designate) need direct Layer 2 connectivity. They communicate using multicast/broadcast packets, so they must be in the same subnet (same broadcast domain). If they're not, the units can't see each other's heartbeats, and the cluster won't form.
This is a hard requirement for FGCP heartbeat communication.
✅ Same HA group ID (D):
The group ID must match exactly on all members. It's used during discovery and negotiation—FortiGates only form a cluster with others that have the identical group ID (along with matching mode, password, etc.). Different group IDs mean they ignore each other, even if physically connected.
This is explicitly required for cluster formation.
Why the others are not required:
A. Same hard drive configuration:
Yes, hardware must generally match (same model, same number of hard disks, same firmware, etc.), but the exact "configuration" (like RAID setup or partitioning) doesn't have to be identical for the cluster to form. The base hardware match is needed for sync and operation, but this option is worded too specifically and isn't a strict formation prerequisite like the heartbeat/group ID items.
B. Same number of configured VDOMs:
This is a common misconception. The number of configured (enabled/created) VDOMs doesn't need to match for HA to form. What matters is the VDOM mode (single vs multi) and having compatible VDOM licenses if using more than the base allowance. But mismatched counts of actual configured VDOMs won't prevent cluster formation—the configs sync anyway.
Reference:
FortiOS 7.6 Administration Guide → High Availability section (specifically FGCP overview and HA heartbeat interface pages):
→ Docs confirm identical HA settings (group-id, password, mode) are required for negotiation.
→ Heartbeat interfaces must share the same broadcast domain/subnet for communication.
→ Hardware parity (model, firmware, disk count) is listed, but not "configuration" details or exact VDOM count as blockers for initial cluster formation.
| Page 1 out of 8 Pages |
| 1234 |
Choosing the right preparation material is critical for passing the Fortinet NSE 4 FortiOS 7.6 Administrator exam. Here’s how our NSE4_FGT_AD-7.6 practice test is designed to bridge the gap between knowledge and a passing score.