Last Updated On : 13-Jan-2026
Total 81 Questions
Which two statements about the Hub Selection Method in FortiSASE Secure Private Access (SPA) are correct? (Choose two answers)
A. When using Hub Health and Priority, FortiSASE selects the highest priority hub that meets the configured SLA thresholds.
B. When using BGP MED, FortiSASE selects the hub with the lowest MED value only if it also meets the configured SLA thresholds.
C. When using SLA thresholds, administrators can customize latency, jitter, and packet loss for each security POP.
D. When using Hub Health and Priority, all hubs with the same priority are always selected regardless of SLA results.
Explanation:
FortiSASE Secure Private Access (SPA) hub selection methods determine optimal connectivity between FortiSASE PoPs and customer hubs using health monitoring, priority, BGP attributes, and customizable SLA parameters. Administrators configure these methods to balance performance, availability, and routing efficiency for private application access. Proper hub selection ensures low-latency, reliable connections while meeting business continuity requirements.
✅ Correct Answer: A
Hub Health and Priority method prioritizes hubs based on configured priority levels while monitoring SLA thresholds like latency, jitter, and packet loss. FortiSASE selects the highest priority hub meeting all SLA requirements, ensuring optimal performance. If the top-priority hub fails SLA checks, it automatically fails over to the next highest priority hub meeting thresholds, providing intelligent load balancing and redundancy.
✅ Correct Answer: B
BGP MED (Multi-Exit Discriminator) selection favors hubs advertising the lowest MED value among BGP peers, but only if they satisfy configured SLA thresholds. This combines BGP path preference with real-time health monitoring, preventing suboptimal routing to unhealthy hubs. FortiSASE first validates SLA compliance before applying MED-based selection, ensuring both policy adherence and network performance.
❌ Incorrect answer: C
SLA thresholds customization occurs at the global or service connection level, not individually per security PoP. PoP-specific customization would create management complexity and inconsistent monitoring. Administrators define uniform SLA parameters applied across all PoPs connecting to specific hubs, maintaining consistent performance standards organization-wide.
❌ Incorrect answer: D
Hub Health and Priority does not select all same-priority hubs regardless of SLA results. It monitors each hub's health individually against SLA thresholds. Only hubs meeting SLA requirements participate in traffic forwarding, even among same-priority group. Unhealthy hubs are excluded until they recover, preventing poor performance from impacting user experience.
Reference:
Fortinet FortiSASE Documentation - Secure Private Access Administration Guide
When configuring the DLP rule in FortiSASE using Regex format, what would be the correct order for the
configuration steps? (Place the four correct steps in order)


You are designing a new network for Company X and one of the new cybersecurity policy requirements is that all remote user endpoints must always be connected and protected Which FortiSASE component facilitates this always-on security measure?
A. site-based deployment
B. thin-branch SASE extension
C. unified FortiClient
D. inline-CASB
Explanation:
Summary
This question evaluates knowledge of how FortiSASE enforces continuous security for remote endpoints. The requirement “always connected and protected” points to endpoint-level enforcement rather than network- or cloud-based inspection. The correct answer must provide persistent connectivity, posture awareness, and automatic security enforcement regardless of user location, which is a core design principle of Fortinet’s zero-trust and SASE architecture.
✅ Correct Answer: C. unified FortiClient
Unified FortiClient is the endpoint agent that enables always-on security in FortiSASE. It maintains persistent, automatic connectivity to the FortiSASE cloud, enforces security posture checks, and ensures traffic is continuously inspected and protected, even when users roam between networks. Without user intervention, FortiClient applies VPN, ZTNA, and security policies, making it the only component designed for mandatory, always-connected endpoint protection.
❌ Incorrect Answer: A. site-based deployment
Site-based deployment applies to fixed locations such as branch offices or data centers. It does not provide per-user, always-on protection for roaming endpoints. Remote users outside the site would remain unprotected unless additional endpoint agents or tunnels are deployed. This model contradicts the requirement that all remote endpoints must remain continuously connected regardless of location.
❌ Incorrect Answer: B. thin-branch SASE extension
Thin-branch SASE extensions are intended for small or lightweight branch offices, not individual remote users. They extend SASE services to a physical location but do not enforce always-on connectivity at the endpoint level. Users connecting from home or mobile networks would not be guaranteed continuous protection using this approach alone.
❌ Incorrect Answer: D. inline-CASB
Inline CASB focuses on controlling and inspecting SaaS application traffic, not on maintaining continuous endpoint connectivity. It operates within the cloud security stack but depends on other components to steer traffic. CASB alone cannot ensure that remote endpoints are always connected or protected, making it insufficient for this requirement.
Reference
Fortinet FortiSASE Administration Guide
Fortinet FortiClient Administration Guide
Fortinet Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) Technical Documentation
Refer to the exhibit.
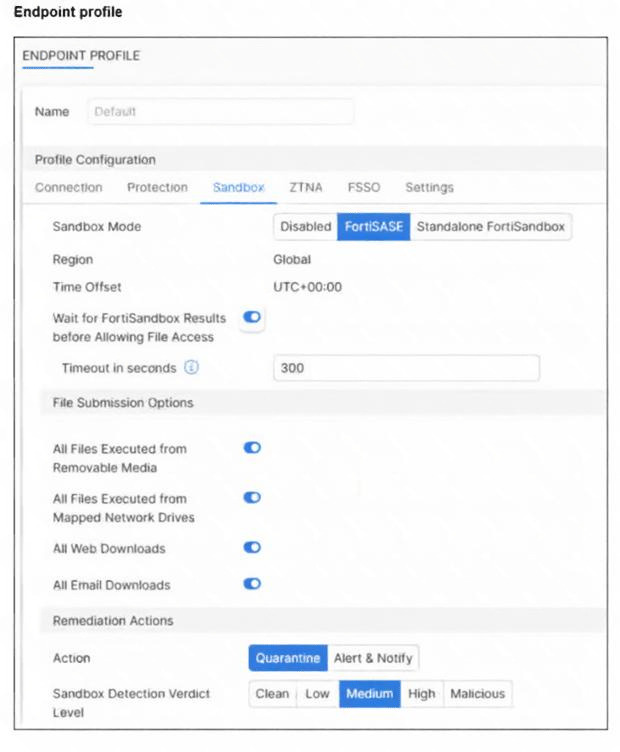
Based on the configuration shown, in which two ways will FortiSASE process sessions that require
FortiSandbox inspection? (Choose two answers)
A. All files will be sent to an on-premises FortiSandbox for inspection.
B. FortiClient quarantines only infected files that FortiSandbox detects as medium level.
C. All files executed on a USB drive will be sent to FortiSandbox for analysis.
D. Only endpoints assigned a profile for sandbox detection will be processed by the sandbox feature.
Explanation:
Summary
The exhibit shows a FortiSASE endpoint profile's Sandbox configuration. The key settings are "Sandbox Mode" set to FortiSASE, "Region" set to Global, and specific "File Submission Options" checked. Understanding these settings is crucial to determining how files are routed for sandbox inspection.
✅ Correct Answers:
C. All files executed on a USB drive will be sent to FortiSandbox for analysis.
This is correct. Under the File Submission Options section, the box for "All Files Executed from Removable Media" is checked. Removable media, such as USB drives, are included in this category. Therefore, any file executed from such a source will be submitted to the sandbox for inspection according to the profile's behavior.
D. Only endpoints assigned a profile for sandbox detection will be processed by the sandbox feature.
This is correct based on FortiSASE's operational principle. Sandbox inspection is a policy-driven feature. An endpoint must be assigned an endpoint profile (like the "Default" profile shown) that has Sandbox Mode enabled (i.e., not set to "Disabled") for its traffic to be eligible for sandbox inspection. Endpoints without such a profile assignment will not have their sessions processed by the sandbox feature.
❌ Incorrect Answers:
A. All files will be sent to an on-premises FortiSandbox for inspection.
This is incorrect. The "Sandbox Mode" is explicitly set to "FortiSASE", not "Standalone FortiSandbox". This means the inspection is performed by the FortiSandbox cloud service integrated into FortiSASE's global infrastructure, not by a customer's on-premises FortiSandbox appliance.
B. FortiClient quarantines only infected files that FortiSandbox detects as medium level.
This is incorrect. The "Remediation Actions" section shows the Action is set to "Quarantine". The "Sandbox Detection Verdict Level" scale below it shows checkboxes selected from Low through Malicious. The "Clean" verdict is the only one unchecked. This configuration means files detected at Low, Medium, High, and Malicious verdict levels will be quarantined, not just those at the "Medium" level.
Reference:
Fortinet Documentation Library: FortiSASE Administration Guide, specifically the sections explaining Endpoint Profile configuration, Sandbox settings, File Submission Options, and remediation actions based on verdict levels.
Refer to the exhibits.
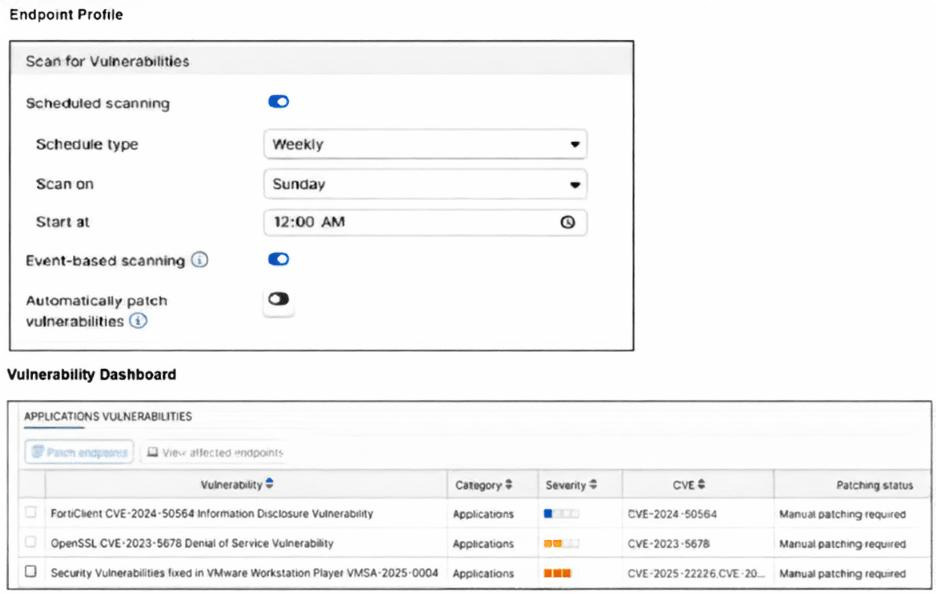
How will the application vulnerabilities be patched, based on the exhibits provided? (Choose one answer)
A. An administrator will patch the vulnerability remotely using FortiSASE.
B. The end user will patch the vulnerabilities using the FortiClient software.
C. The vulnerability will be patched by installing the patch from the vendor's website.
D. The vulnerability will be patched automatically based on the endpoint profile configuration.
Explanation:
The exhibit highlights the Vulnerability Summary dashboard in FortiSASE, which provides visibility into security weaknesses across managed endpoints. In the FortiSASE ecosystem, while the FortiClient agent performs the actual scan, the administrator has the authority to initiate remediation directly from the management console for specific vulnerabilities. This centralized control allows for targeted patching without relying on the end-user to manually find or execute updates from external vendor websites.
✅ Correct Answer:
Option A: In FortiSASE, an administrator can view a drill-down of specific vulnerabilities (such as those for the OS or third-party applications) and select affected endpoints to trigger a patch. By right-clicking a vulnerability or using the "Patch" action menu within the dashboard, the administrator can remotely command the FortiClient agent to download and install the necessary security update. This ensures that critical security gaps are closed efficiently through a centralized administrative action.
❌ Incorrect Answers:
Option B: While the FortiClient software on the endpoint displays detected vulnerabilities to the user, the standard enterprise workflow in FortiSASE emphasizes centralized management. Relying on the end user to patch vulnerabilities is not the primary mechanism depicted in the administrative exhibits, as it leads to inconsistent security postures across the organization.
Option C: Although patches ultimately originate from a vendor's website, the "patching" process referred to in the context of FortiSASE dashboard actions is the automated orchestration through the platform. Telling a user to manually navigate to a vendor site and install a patch defeats the purpose of the integrated vulnerability management and remediation features provided by the FortiSASE/FortiClient EMS integration.
Option D: Vulnerabilities can be patched automatically if the "Automatic Patching" toggle is enabled within the Endpoint Profile. However, in many exam scenarios and real-world configurations, this is often disabled to prevent unplanned reboots or application compatibility issues. When "Manual Patching Required" is indicated or when the administrator is performing the action from the dashboard, it is a manual administrative trigger rather than a fully autonomous profile-based event.
Reference:
Official Fortinet Documentation: FortiSASE - Vulnerability Summary
Official Fortinet Documentation: Patching Vulnerabilities on Endpoints
During FortiSASE provisioning, how many security points of presence (POPs) need to be configured by the FortiSASE administrator?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 2
D. 1
Explanation:
This question tests your understanding of FortiSASE initial provisioning requirements, specifically how many security Points of Presence must be configured during setup. Starting with FortiSASE 24.2, support was added for provisioning instances with fewer security PoPs, removing the previous restriction to select four security PoPs. The minimum requirement changed based on license type and version, making this a critical detail for the NSE7 exam.
✅ Correct Answer: D - 1
During initial provisioning, administrators can select fewer security sites than the maximum they are entitled to, and Comprehensive licenses are entitled to only 1 PoP. This flexibility allows organizations to start with minimal infrastructure and scale as needed. A single security PoP provides all necessary security services including firewall, secure web gateway, and threat intelligence for remote users to begin using FortiSASE immediately. One PoP is sufficient to get started with FortiSASE, providing the necessary security services and connectivity for users Fortinet. Organizations can add additional PoPs post-deployment for redundancy and geographic coverage.
❌ Incorrect Answer: A - 3
Three PoPs is not a FortiSASE requirement during initial provisioning. While having three locations might provide good geographic distribution, FortiSASE doesn't mandate this specific number. The platform is designed to be flexible, allowing administrators to provision based on their license entitlement and business needs rather than arbitrary fixed numbers. The confusion might arise from older deployment best practices, but the actual minimum requirement is one PoP, not three.
❌ Incorrect Answer: B - 4
Four PoPs was historically shown in older provisioning interfaces but has never been a mandatory minimum. The provisioning screen might display "0/4" during setup, indicating you can choose up to 4 PoPs, but this represents the maximum for certain license types, not the minimum required. Earlier FortiSASE versions encouraged selecting four locations for optimal coverage, but version 24.2 explicitly removed any such restriction, making it clear that four is not required.
❌ Incorrect Answer: C - 2
Two PoPs appears in documentation specifically for redundancy recommendations but is not the baseline provisioning requirement. Some older documentation stated that Standard and Advanced licenses should provision two to four data centers for redundancy purposes, but this was guidance rather than a hard requirement. The actual minimum you need to configure during provisioning is one PoP. Two PoPs would provide failover capability, but it's not mandatory to complete initial setup.
Which policy type is used to control traffic between the FortiClient endpoint to FortiSASE for secure internet access?
A. VPN policy
B. thin edge policy
C. private access policy
D. secure web gateway (SWG) policy
Explanation:
To enable secure internet access for FortiClient endpoints via FortiSASE, traffic is inspected and controlled using a Secure Web Gateway (SWG) policy. This policy enforces web filtering, malware inspection, and other security controls on internet-bound traffic before it exits to the public internet.
✅ Correct Answer:
D. Secure Web Gateway (SWG) policy
The Secure Web Gateway (SWG) policy in FortiSASE governs how internet-bound traffic from FortiClient endpoints is handled. It applies security services such as URL filtering, antivirus scanning, sandboxing, and application control to protect users accessing the internet. This policy is essential for enforcing secure internet access when endpoints are off the corporate network and routing traffic through FortiSASE’s cloud-delivered security stack.
❌ Incorrect Answers:
A. VPN policy
While a VPN policy defines how endpoints establish secure tunnels to FortiSASE or other gateways, it does not control or inspect internet-bound traffic. Its role is limited to tunnel establishment and routing, not content inspection or web security enforcement.
B. Thin edge policy
This is not a standard policy type in FortiSASE. Fortinet documentation does not reference “thin edge policy” as a valid configuration object for traffic control between FortiClient and FortiSASE, making this option invalid.
C. Private access policy
Private Access policies in FortiSASE are used to control access to internal private applications (e.g., SaaS or on-premises apps) via ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access). They do not apply to general internet traffic or secure web browsing scenarios.
Reference:
Fortinet official documentation - FortiSASE
| Page 2 out of 12 Pages |
| NSE7_SSE_AD-25 Practice Test Home |
Choosing the right preparation material is critical for passing the Fortinet Fortinet NSE 7 - FortiSASE 25 Enterprise Administrator exam. Here’s how our NSE7_SSE_AD-25 practice test is designed to bridge the gap between knowledge and a passing score.